Problem of The Day: Map of Highest Peak
Problem Statement
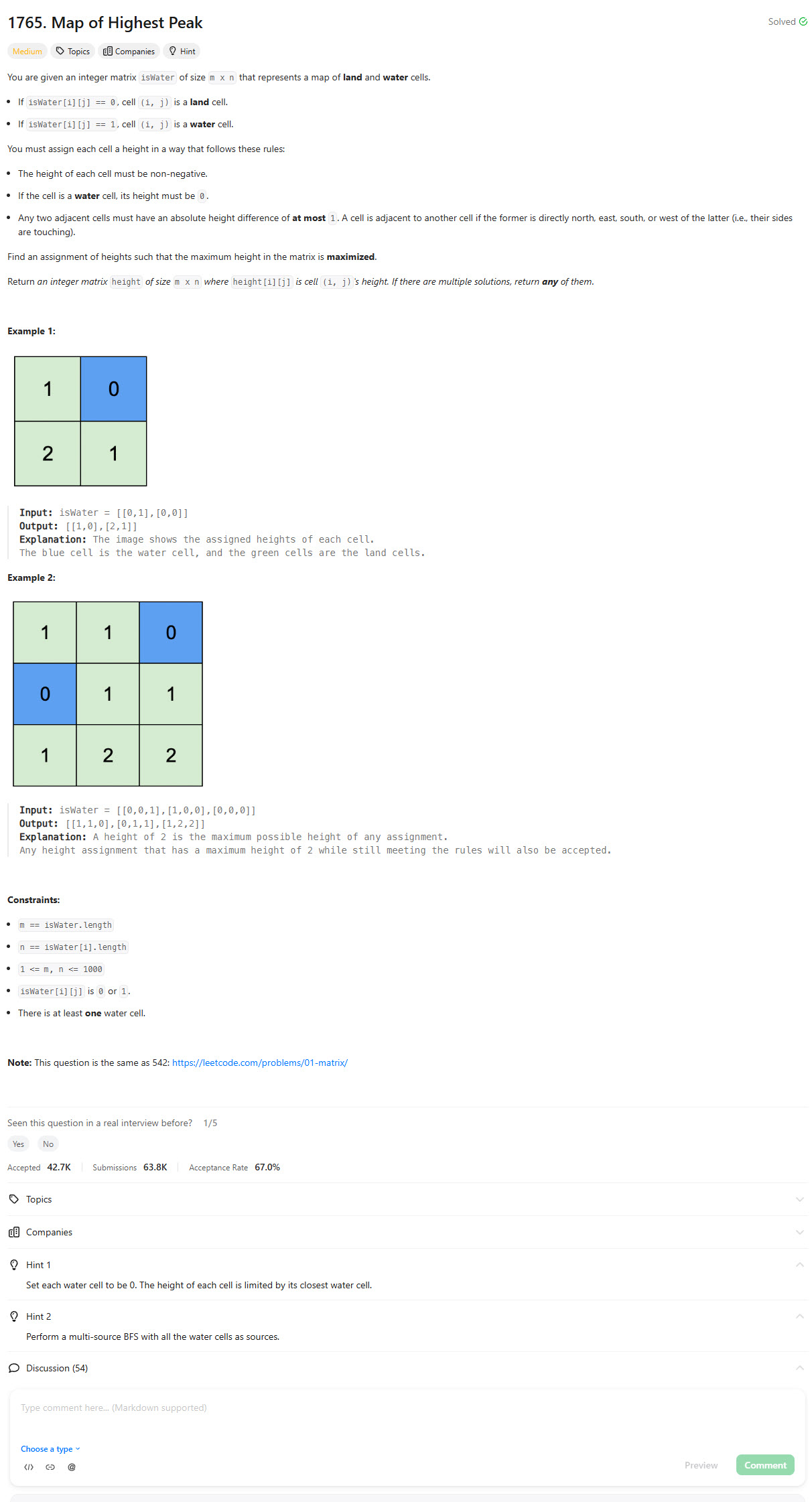
BFS Approach [Accepted]
class Solution:
def highestPeak(self, isWater: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
queue = deque()
ROWS = len(isWater)
COLS = len(isWater[0])
set_cells = set()
for row in range(ROWS):
for col in range(COLS):
if isWater[row][col] == 1:
isWater[row][col] = 0
queue.append([row, col])
set_cells.add((row, col))
h = 1
while queue:
n = len(queue)
for _ in range(n):
r, c = queue.popleft()
for x, y in [(0,1),(1,0),(-1,0),(0,-1)]:
nr, nc = r + x, c + y
if 0 <= nr < ROWS and 0 <= nc < COLS and (nr, nc) not in set_cells:
isWater[nr][nc] = h
set_cells.add((nr, nc))
queue.append([nr, nc])
h += 1
return isWater
Editorial
Approach 1: Breadth-first search
class Solution:
def highestPeak(self, is_water):
dx = [0, 0, 1, -1] # Horizontal movement: right, left, down, up
dy = [1, -1, 0, 0] # Vertical movement corresponding to dx
rows = len(is_water)
columns = len(is_water[0])
# Initialize the height matrix with -1 (unprocessed cells)
cell_heights = [[-1 for _ in range(columns)] for _ in range(rows)]
# Queue to perform breadth-first search
cell_queue = deque()
# Add all water cells to the queue and set their height to 0
for x in range(rows):
for y in range(columns):
if is_water[x][y] == 1:
cell_queue.append((x, y))
cell_heights[x][y] = 0
# Initial height for land cells adjacent to water
height_of_next_layer = 1
# Perform BFS
while cell_queue:
layer_size = len(cell_queue)
# Iterate through all cells in the current layer
for _ in range(layer_size):
current_cell = cell_queue.popleft()
# Check all four possible directions for neighboring cells
for d in range(4):
neighbor_x = current_cell[0] + dx[d]
neighbor_y = current_cell[1] + dy[d]
# Check if the neighbor is valid and unprocessed
if (
self._is_valid_cell(
neighbor_x, neighbor_y, rows, columns
)
and cell_heights[neighbor_x][neighbor_y] == -1
):
cell_heights[neighbor_x][
neighbor_y
] = height_of_next_layer
cell_queue.append((neighbor_x, neighbor_y))
height_of_next_layer += 1 # Increment height for the next layer
return cell_heights
def _is_valid_cell(self, x, y, rows, columns):
"""Check if a cell is within the grid boundaries."""
return 0 <= x < rows and 0 <= y < columns
Approach 2: Dynamic Programming
class Solution:
def highestPeak(self, is_water: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
rows = len(is_water)
columns = len(is_water[0])
INF = rows * columns # Large value to represent uninitialized heights
# Initialize the cellHeights matrix with INF (unprocessed cells)
cell_heights = [[INF] * columns for _ in range(rows)]
# Set the height of water cells to 0
for row in range(rows):
for col in range(columns):
if is_water[row][col] == 1:
cell_heights[row][col] = 0 # Water cells have height 0
# Forward pass: updating heights based on top and left neighbors
for row in range(rows):
for col in range(columns):
# Initialize minimum neighbor distance
min_neighbor_distance = INF
# Check the cell above
neighbor_row = row - 1
neighbor_col = col
if self.is_valid_cell(
neighbor_row, neighbor_col, rows, columns
):
min_neighbor_distance = min(
min_neighbor_distance,
cell_heights[neighbor_row][neighbor_col],
)
# Check the cell to the left
neighbor_row = row
neighbor_col = col - 1
if self.is_valid_cell(
neighbor_row, neighbor_col, rows, columns
):
min_neighbor_distance = min(
min_neighbor_distance,
cell_heights[neighbor_row][neighbor_col],
)
# Set the current cell's height as the minimum of its neighbors + 1
cell_heights[row][col] = min(
cell_heights[row][col], min_neighbor_distance + 1
)
# Backward pass: updating heights based on bottom and right neighbors
for row in range(rows - 1, -1, -1):
for col in range(columns - 1, -1, -1):
# Initialize minimum neighbor distance
min_neighbor_distance = INF
# Check the cell below
neighbor_row = row + 1
neighbor_col = col
if self.is_valid_cell(
neighbor_row, neighbor_col, rows, columns
):
min_neighbor_distance = min(
min_neighbor_distance,
cell_heights[neighbor_row][neighbor_col],
)
# Check the cell to the right
neighbor_row = row
neighbor_col = col + 1
if self.is_valid_cell(
neighbor_row, neighbor_col, rows, columns
):
min_neighbor_distance = min(
min_neighbor_distance,
cell_heights[neighbor_row][neighbor_col],
)
# Set the current cell's height as the minimum of its neighbors + 1
cell_heights[row][col] = min(
cell_heights[row][col], min_neighbor_distance + 1
)
return cell_heights # Return the calculated cell heights
# Function to check if a cell is within grid bounds
def is_valid_cell(
self, row: int, col: int, rows: int, columns: int
) -> bool:
return 0 <= row < rows and 0 <= col < columns