Problem of The Day: Find Largest Value in Each Tree Row
Problem Statement
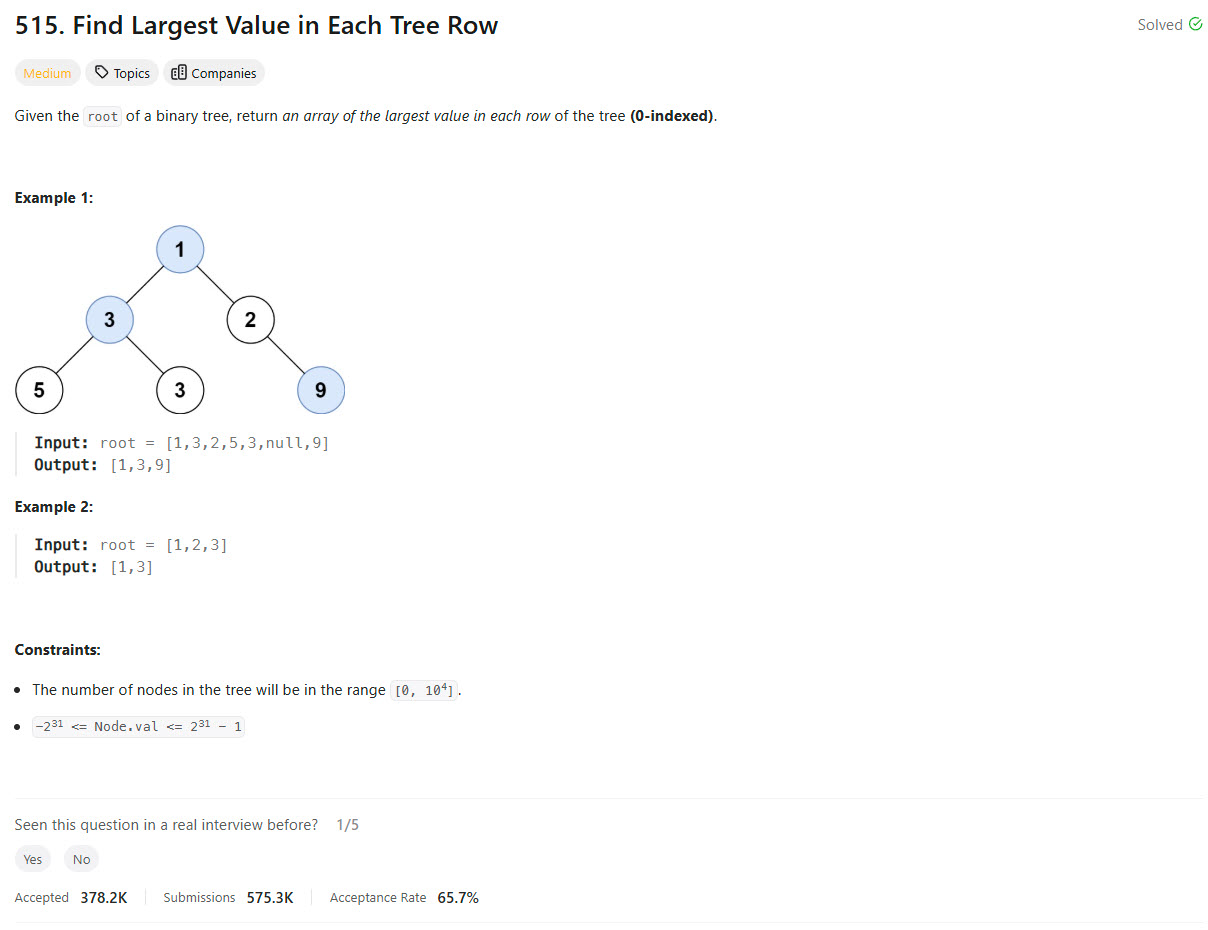
Intuition
The problem requires finding the largest value in each row of a binary tree. The first thought is to traverse the tree level by level (breadth-first search), keeping track of the largest value encountered at each level.
Approach
- Use a queue to perform a breadth-first search (BFS) on the tree.
- At each level:
- Determine the number of nodes at that level.
- Iterate through the nodes, keeping track of the maximum value encountered.
- Add the children of each node to the queue for processing in the next level.
- Append the maximum value of the current level to the result list.
- Continue until all levels are processed.
- Return the result list containing the largest values for each row.
Complexity
-
Time complexity:
\(O(n)\)
Each node in the tree is visited once, where \(n\) is the number of nodes in the binary tree. -
Space complexity:
\(O(w)\)
The space complexity depends on the maximum width of the tree \(w\), which is the maximum number of nodes in any level of the binary tree.
Code
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def largestValues(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
res = []
queue = deque([root])
while queue:
n = len(queue)
curr_max = float('-inf')
for _ in range(n):
node = queue.popleft()
if node:
curr_max = max(curr_max, node.val)
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
if curr_max != float('-inf'):
res.append(curr_max)
return res
Editorial
Approach 1: Breadth First Search (BFS)
class Solution:
def largestValues(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
if not root:
return []
ans = []
queue = deque([root])
while queue:
current_length = len(queue)
curr_max = float("-inf")
for _ in range(current_length):
node = queue.popleft()
curr_max = max(curr_max, node.val)
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
ans.append(curr_max)
return ans
```
Approach 2: Depth First Search (DFS)
class Solution:
def largestValues(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
def dfs(node, depth):
if not node:
return
if depth == len(ans):
ans.append(node.val)
else:
ans[depth] = max(ans[depth], node.val)
dfs(node.left, depth + 1)
dfs(node.right, depth + 1)
ans = []
dfs(root, 0)
return ans