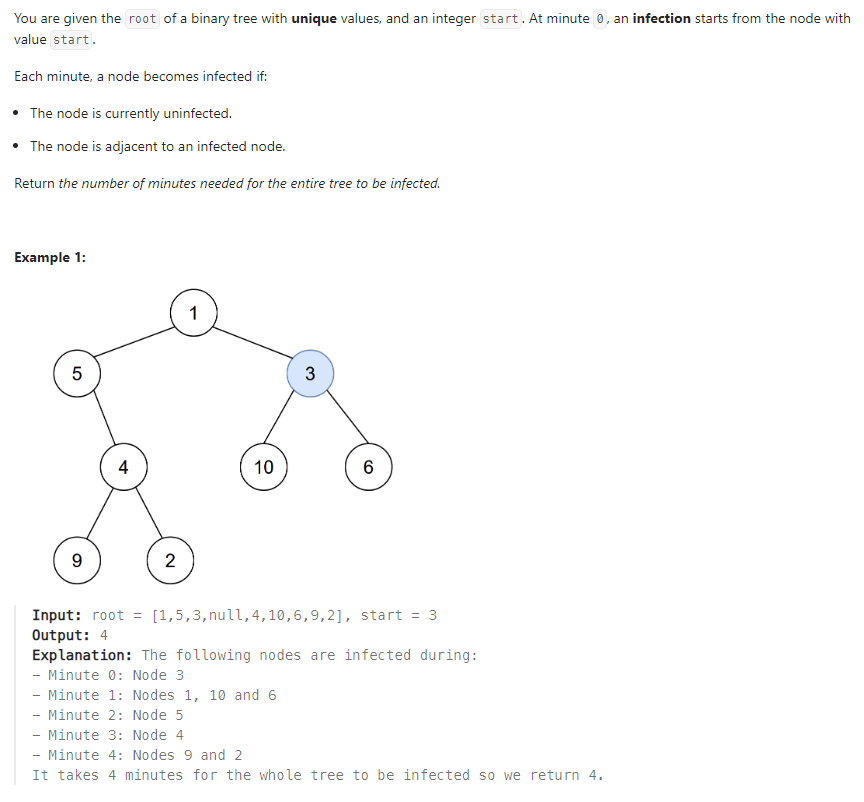
Problem of The Day: Amount of Time for Binary Tree to Be Infected
Problem statement
Intuition
The problem involves calculating the amount of time it takes for a contagion to spread throughout a binary tree starting from a given node. The goal is to build a graph representing the connections between nodes in the tree and then simulate the spread of infection using a breadth-first search (BFS) approach.
Approach
The solution first defines a helper function build_graph to construct an undirected graph based on the binary tree. The function utilizes a breadth-first traversal of the tree, populating the graph with edges between nodes and their respective parents. After building the graph, the main function amountOfTime performs a BFS starting from the specified node (start). The BFS keeps track of the infected nodes and increments the time (in minutes) until all reachable nodes are infected.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(N), where N is the number of nodes in the binary tree. Both building the graph and performing BFS involve visiting each node once.
-
Space complexity: O(N), as we use additional data structures (queues, sets, and the graph) to store information about the nodes.
Code
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def build_graph(self, root):
# Helper function to build an undirected graph from the binary tree
queue = deque()
queue.append([root, None])
graph = defaultdict(list)
while queue:
node, parent = queue.popleft()
if parent:
graph[parent.val].append(node.val)
graph[node.val].append(parent.val)
if node:
if node.left:
queue.append([node.left, node])
if node.right:
queue.append([node.right, node])
return graph
def amountOfTime(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], start: int) -> int:
graph = self.build_graph(root)
queue = deque()
queue.append(start)
infect = set()
infect.add(start)
minute = 0
while queue:
n = len(queue)
for _ in range(n):
node = queue.popleft()
infect.add(node)
for nei in graph[node]:
if nei not in infect:
queue.append(nei)
minute += 1
return minute - 1
Editorial Code
One pass with DFS
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.max_distance = 0
def amountOfTime(self, root, start):
self.traverse(root, start)
return self.max_distance
def traverse(self, root, start):
depth = 0
if root is None:
return depth
left_depth = self.traverse(root.left, start)
right_depth = self.traverse(root.right, start)
if root.val == start:
self.max_distance = max(left_depth, right_depth)
depth = -1
elif left_depth >= 0 and right_depth >= 0:
depth = max(left_depth, right_depth) + 1
else:
distance = abs(left_depth) + abs(right_depth)
self.max_distance = max(self.max_distance, distance)
depth = min(left_depth, right_depth) - 1
return depth