Problem of The Day: Binary Subarrays With Sum
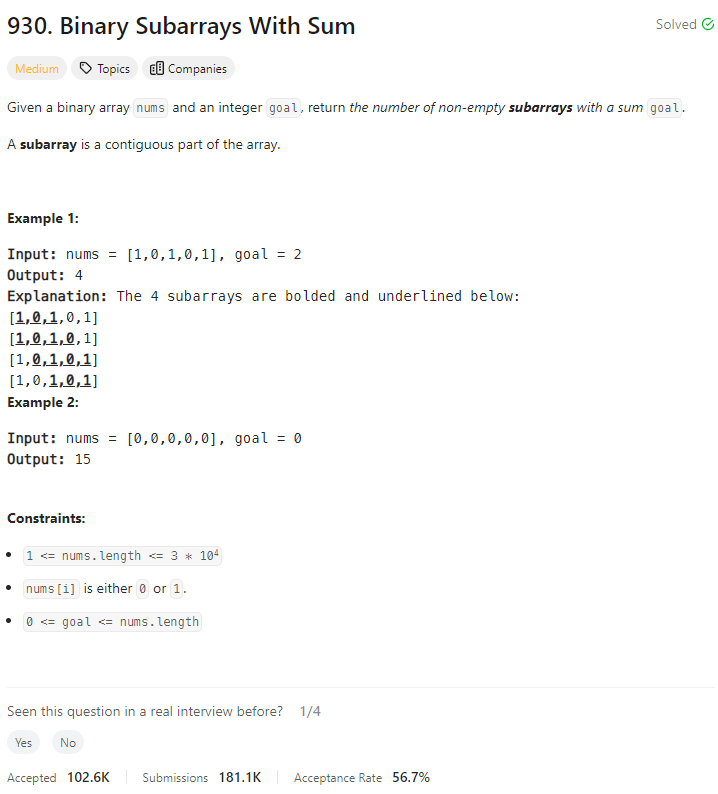
Problem Statement
Brute Force - TLE
class Solution:
def numSubarraysWithSum(self, nums: List[int], goal: int) -> int:
N = len(nums)
res = 0
for i in range(N):
curr_sum = 0
for j in range(i, N):
curr_sum += nums[j]
if curr_sum == goal:
res += 1
return res
- Time complexity: O(n^2)
- Space complexity: O(1)
Prefix Sum/Hash map Approach
Intuition
My thought is to utilize a sliding window approach combined with prefix sums to efficiently count the number of subarrays with a given sum.
Approach
I’ll maintain a running sum as I iterate through the array. At each step, I’ll check if the current sum equals the target sum. If it does, I’ll increment the count of valid subarrays. Additionally, I’ll keep track of the frequency of prefix sums encountered so far. If the difference between the current sum and the target sum has been seen before, I’ll add the corresponding frequency to the count of valid subarrays.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(n) where n is the length of the input array. We traverse the array once.
-
Space complexity: O(n) where n is the length of the input array. We use a dictionary to store the frequency of prefix sums encountered.
Code
class Solution:
def numSubarraysWithSum(self, nums: List[int], goal: int) -> int:
N = len(nums)
res = 0
curr_sum = 0
prefix_sum = defaultdict(int)
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
curr_sum += num
if curr_sum == goal:
res += 1
if curr_sum - goal in prefix_sum:
res += prefix_sum[curr_sum - goal]
prefix_sum[curr_sum] += 1
return res
Editorial Solution
Approach 1: Prefix Sum
class Solution:
def numSubarraysWithSum(self, nums: List[int], goal: int) -> int:
total_count = 0
current_sum = 0
# {prefix: number of occurrence}
freq = {} # To store the frequency of prefix sums
for num in nums:
current_sum += num
if current_sum == goal:
total_count += 1
# Check if there is any prefix sum that can be subtracted from the current sum to get the desired goal
if current_sum - goal in freq:
total_count += freq[current_sum - goal]
freq[current_sum] = freq.get(current_sum, 0) + 1
return total_count
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(n)
Approach 2: Sliding Window
class Solution:
# Helper function to count the number of subarrays with sum at most the given goal
def sliding_window_at_most(self, nums: List[int], goal: int) -> int:
start, current_sum, total_count = 0, 0, 0
# Iterate through the array using a sliding window approach
for end in range(len(nums)):
current_sum += nums[end]
# Adjust the window by moving the start pointer to the right
# until the sum becomes less than or equal to the goal
while start <= end and current_sum > goal:
current_sum -= nums[start]
start += 1
# Update the total count by adding the length of the current subarray
total_count += end - start + 1
return total_count
def numSubarraysWithSum(self, nums: List[int], goal: int) -> int:
return self.sliding_window_at_most(nums, goal) - self.sliding_window_at_most(nums, goal - 1)
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)