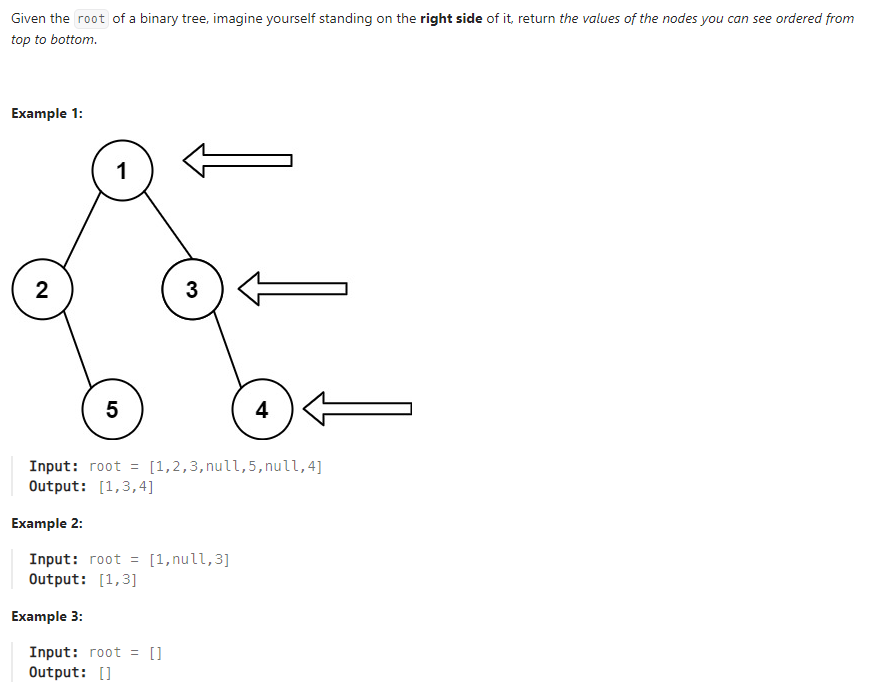
Problem: Binary Tree Right Side View
Problem Statement
Intuition
The problem suggests finding the right side view of a binary tree, indicating a level-order traversal (BFS) approach. My initial thoughts involve traversing the tree level by level and capturing the rightmost element at each level.
Approach
The problem at hand is to determine the right side view of a binary tree, signifying that for each level of the tree, we need to capture and return the rightmost element. My approach to solving this involves utilizing a level-order traversal, or breadth-first search (BFS). I will employ a queue to traverse the tree level by level, starting with the root. While traversing each level, I’ll keep track of the rightmost element encountered, and after completing a level, I’ll append this rightmost element to the result list. To ensure a correct order of traversal, I’ll enqueue the child nodes of the current level, prioritizing the right child before the left child. This process continues until all levels have been traversed, and the final result is a list containing the right side view elements of the binary tree.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree. Each node is visited once during the traversal.
-
Space complexity: O(m), where m is the maximum number of nodes at any level in the binary tree. In the worst case, the queue can contain all nodes at a certain level.
Code
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rightSideView(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
if not root:
return []
result = []
queue = deque()
queue.append(root)
while queue:
result.append(queue[-1].val)
n = len(queue)
for _ in range(n):
node = queue.popleft()
if node:
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return result
Editorial Solution
This algorithm utilizes a similar approach to the previous one, aiming to find the right side view of a binary tree through a level-order traversal. However, instead of using a single queue, it employs two queues: curr_level and next_level. The outer loop iterates through each level, and the inner loop processes nodes within the current level. For each node, its children are enqueued into the next_level queue, ensuring a proper order for traversal. After processing the current level, the rightmost node is added to the result list. This dual-queue structure helps in efficiently managing the traversal without the need for a separate counter to track levels. The time complexity remains O(n), where n is the number of nodes, and the space complexity is O(m), where m is the maximum number of nodes at any level in the tree.
class Solution:
def rightSideView(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
if root is None:
return []
next_level = deque([root,])
rightside = []
while next_level:
# prepare for the next level
curr_level = next_level
next_level = deque()
while curr_level:
node = curr_level.popleft()
# add child nodes of the current level
# in the queue for the next level
if node.left:
next_level.append(node.left)
if node.right:
next_level.append(node.right)
# The current level is finished.
# Its last element is the rightmost one.
rightside.append(node.val)
return rightside