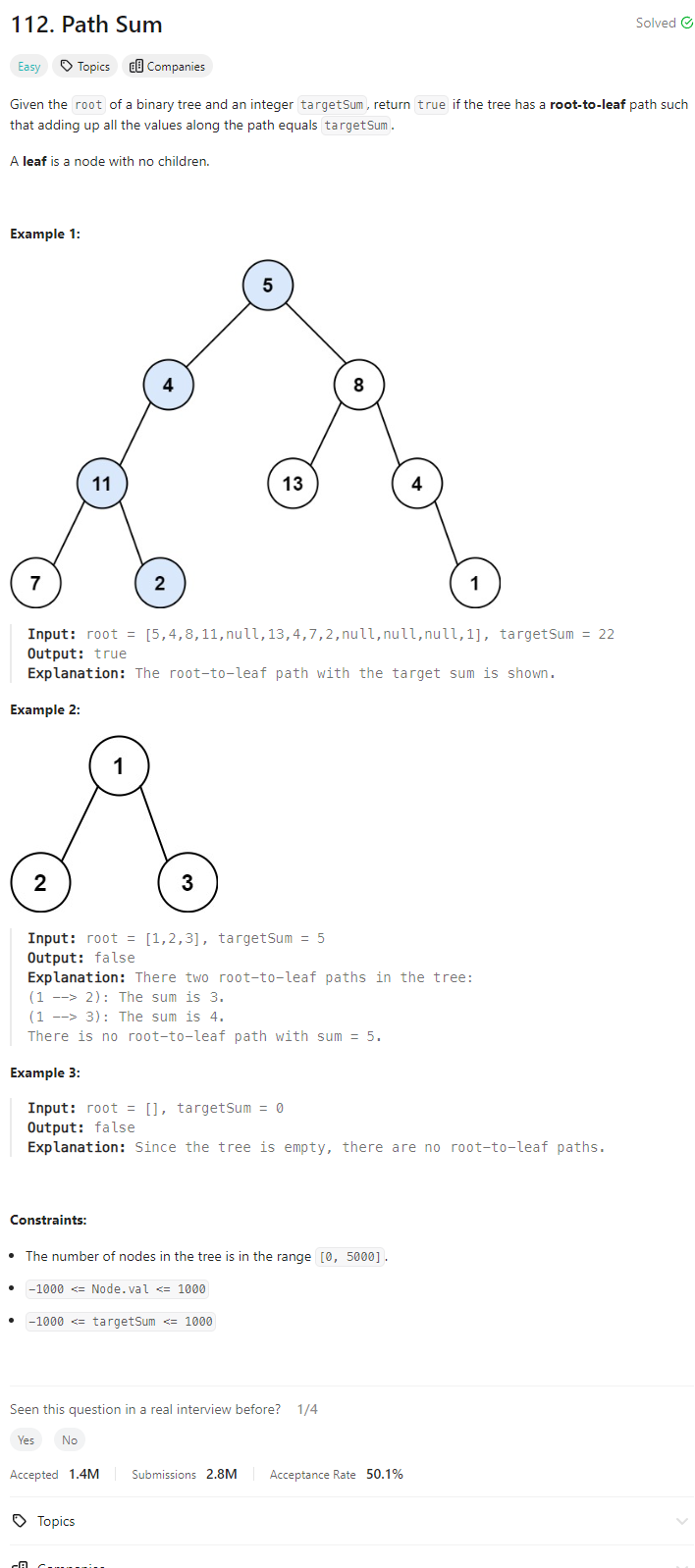
Problem of The Day: Path Sum
Problem Statement
Intuition
My initial thought to solve this problem is to use depth-first search (DFS) traversal. The idea is to traverse the tree recursively and at each node, subtract the node’s value from the target sum. If we reach a leaf node and the remaining target sum equals zero, then we’ve found a path with the given sum.
Approach
I’ll define a recursive function dfs that takes a node and the remaining target sum as arguments. Within this function, I’ll check if the current node is a leaf node and if the remaining target sum equals the node’s value. If both conditions are met, I’ll return True, indicating that a path with the given sum exists. Otherwise, I’ll recursively call the dfs function for the left and right child nodes, subtracting the node’s value from the remaining target sum. If any of these recursive calls return True, then I’ll propagate True up the call stack. If none of the paths satisfy the condition, I’ll return False.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(n) where n is the number of nodes in the tree. We visit each node once.
-
Space complexity: O(h) where h is the height of the binary tree. In the worst case, the space could be O(n) if the tree is skewed
Code
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
def dfs(node, target):
if node and not node.left and not node.right:
return target - node.val == 0
return (node and node.left and dfs(node.left, target - node.val)) or \
(node and node.right and dfs(node.right, target - node.val))
return dfs(root, targetSum)
Same Idea Different Implementation
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
def dfs(node, target):
if not node:
return False
if node and not node.left and not node.right:
return target - node.val == 0
return node.left and dfs(node.left, target - node.val) or \
node.right and dfs(node.right, target - node.val)
return dfs(root, targetSum)
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
def dfs(node, target):
if not node:
return False
if node and not node.left and not node.right:
return target - node.val == 0
L = R = False
if node.left:
L = dfs(node.left, target - node.val)
if node.right:
R = dfs(node.right, target - node.val)
return L or R
return dfs(root, targetSum)
Editorial Solution
Approach 1: Recursion
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if not root:
return False
sum -= root.val
if not root.left and not root.right: # if reach a leaf
return sum == 0
return self.hasPathSum(root.left, sum) or self.hasPathSum(root.right, sum)
Approach 2: Iterations
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if not root:
return False
de = [(root, sum - root.val), ]
while de:
node, curr_sum = de.pop()
if not node.left and not node.right and curr_sum == 0:
return True
if node.right:
de.append((node.right, curr_sum - node.right.val))
if node.left:
de.append((node.left, curr_sum - node.left.val))
return False