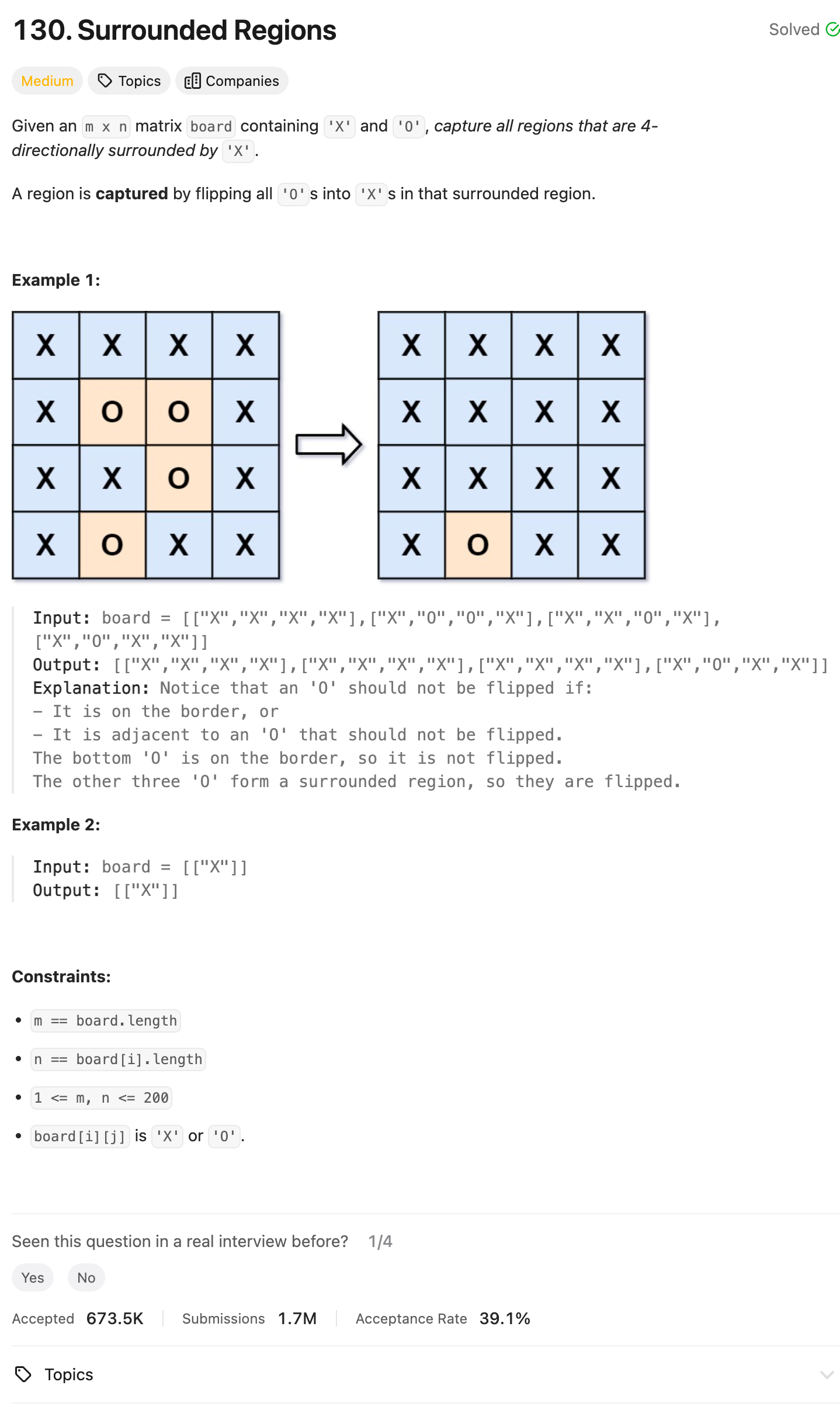
Problem of The Day: Surrounded Regions
Problem Statement
Intuition
The intuition behind this solution is to utilize a Breadth-First Search (BFS) approach to solve the problem.
Approach
Firstly, I initialize a deque to keep track of cells that are adjacent to the borders and are not supposed to be flipped. I iterate through the borders of the board, checking for ‘O’ cells, and add their coordinates to the deque.
Next, I run a BFS loop while there are still unprocessed cells in the deque. I pop a cell from the deque, mark it as ‘2’ to indicate it’s been visited, and explore its neighboring cells. If a neighboring cell is within the bounds of the board and is an ‘O’, I add it to the deque for further processing.
After marking all cells that should not be flipped, I iterate through the entire board again. For each cell, if it’s an ‘O’, I change it to ‘X’, as it’s surrounded by ‘X’ cells and should be flipped.
Finally, I iterate through the board once more. For cells marked as ‘2’, I change them back to ‘O’, as they are originally ‘O’ cells adjacent to the border and should not be flipped.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(mn), where m is the number of rows and n is the number of columns in the board.
-
Space complexity: O(mn), mainly due to the deque used for BFS traversal.
Code
class Solution:
def solve(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
ROWS = len(board)
COLS = len(board[0])
not_flipped_cells = deque()
for r in range(ROWS):
if board[r][0] == "O":
not_flipped_cells.append([r, 0])
if board[r][COLS - 1] == "O":
not_flipped_cells.append([r, COLS - 1])
for c in range(COLS):
if board[0][c] == "O":
not_flipped_cells.append([0, c])
if board[ROWS - 1][c] == "O":
not_flipped_cells.append([ROWS-1, c])
while not_flipped_cells:
row, col = not_flipped_cells.popleft()
if board[row][col] in ("X", "2"):
continue
board[row][col] = "2"
for x, y in ([0,1],[1,0],[0,-1],[-1,0]):
r, c = row + x, col + y
if 0 <= r < ROWS and 0 <= c < COLS and board[r][c] == "O":
not_flipped_cells.append([r,c])
for r in range(ROWS):
for c in range(COLS):
if board[r][c] == "O":
board[r][c] = "X"
for r in range(ROWS):
for c in range(COLS):
if board[r][c] == "2":
board[r][c] = "O"
Editorial Solution
Approach 1: DFS (Depth-First Search)
class Solution(object):
def solve(self, board):
"""
:type board: List[List[str]]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
if not board or not board[0]:
return
self.ROWS = len(board)
self.COLS = len(board[0])
# Step 1). retrieve all border cells
from itertools import product
borders = list(product(range(self.ROWS), [0, self.COLS-1])) \
+ list(product([0, self.ROWS-1], range(self.COLS)))
# Step 2). mark the "escaped" cells, with any placeholder, e.g. 'E'
for row, col in borders:
self.DFS(board, row, col)
# Step 3). flip the captured cells ('O'->'X') and the escaped one ('E'->'O')
for r in range(self.ROWS):
for c in range(self.COLS):
if board[r][c] == 'O': board[r][c] = 'X' # captured
elif board[r][c] == 'E': board[r][c] = 'O' # escaped
def DFS(self, board, row, col):
if board[row][col] != 'O':
return
board[row][col] = 'E'
if col < self.COLS-1: self.DFS(board, row, col+1)
if row < self.ROWS-1: self.DFS(board, row+1, col)
if col > 0: self.DFS(board, row, col-1)
if row > 0: self.DFS(board, row-1, col)
Approach 2: BFS (Breadth-First Search)
class Solution(object):
def solve(self, board):
"""
:type board: List[List[str]]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
if not board or not board[0]:
return
self.ROWS = len(board)
self.COLS = len(board[0])
# Step 1). retrieve all border cells
from itertools import product
borders = list(product(range(self.ROWS), [0, self.COLS-1])) \
+ list(product([0, self.ROWS-1], range(self.COLS)))
# Step 2). mark the "escaped" cells, with any placeholder, e.g. 'E'
for row, col in borders:
#self.DFS(board, row, col)
self.BFS(board, row, col)
# Step 3). flip the captured cells ('O'->'X') and the escaped one ('E'->'O')
for r in range(self.ROWS):
for c in range(self.COLS):
if board[r][c] == 'O': board[r][c] = 'X' # captured
elif board[r][c] == 'E': board[r][c] = 'O' # escaped
def BFS(self, board, row, col):
from collections import deque
queue = deque([(row, col)])
while queue:
(row, col) = queue.popleft()
if board[row][col] != 'O':
continue
# mark this cell as escaped
board[row][col] = 'E'
# check its neighbor cells
if col < self.COLS-1: queue.append((row, col+1))
if row < self.ROWS-1: queue.append((row+1, col))
if col > 0: queue.append((row, col-1))
if row > 0: queue.append((row-1, col))