Problem of The Day: Clone Graph
Problem Statement
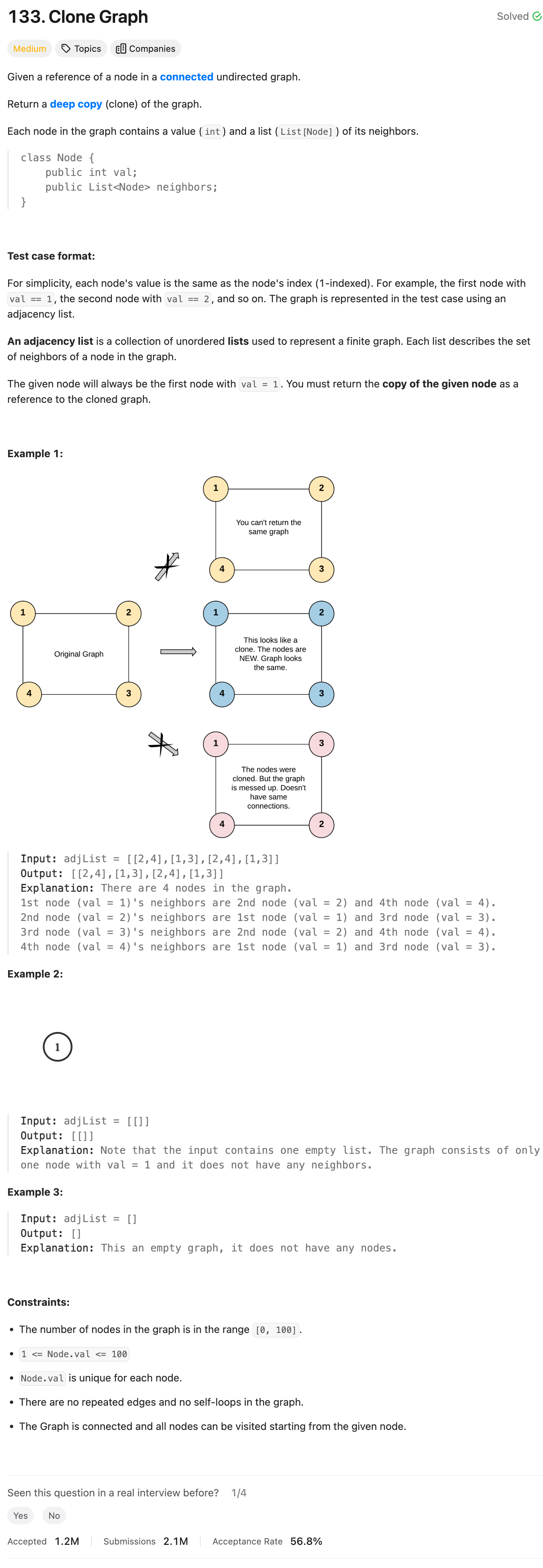
Intuition
My first thought to solve this problem is to traverse the original graph using a depth-first search (DFS) or breadth-first search (BFS) approach. During traversal, I’ll create a new node for each node encountered in the original graph and maintain a mapping between original nodes and their corresponding clones.
Approach
I’ll use a queue (for BFS) to traverse the original graph. As I traverse each node, I’ll create a clone for it and store it in a dictionary where the original node is the key and its clone is the value. This ensures that we don’t create duplicate clones for the same node.
After traversing and cloning all nodes, I’ll iterate through the dictionary again to update the neighbors of each clone. For each original node, I’ll iterate through its neighbors and add the corresponding clones of those neighbors to the clone’s neighbor list.
Finally, I’ll return the clone of the input node (if it exists) from the dictionary. If the input node is None or not in the clones dictionary, I’ll return None.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(V + E) where V is the number of vertices (nodes) and E is the number of edges in the graph.
-
Space complexity: O(V), where V is the number of vertices in the graph.
Code
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val = 0, neighbors = None):
self.val = val
self.neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else []
"""
from typing import Optional
class Solution:
def cloneGraph(self, node: Optional['Node']) -> Optional['Node']:
clones = defaultdict(Node)
queue = deque([node])
while queue:
curr_node = queue.popleft()
if curr_node and curr_node not in clones:
clones[curr_node] = Node(curr_node.val)
for nei in curr_node.neighbors:
queue.append(nei)
for k, v in clones.items():
for nei in k.neighbors:
v.neighbors.append(clones[nei])
return clones[node] if node in clones else None
Editorial Solution
Approach 1: Depth First Search
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, neighbors):
self.val = val
self.neighbors = neighbors
"""
class Solution(object):
def __init__(self):
# Dictionary to save the visited node and it's respective clone
# as key and value respectively. This helps to avoid cycles.
self.visited = {}
def cloneGraph(self, node):
"""
:type node: Node
:rtype: Node
"""
if not node:
return node
# If the node was already visited before.
# Return the clone from the visited dictionary.
if node in self.visited:
return self.visited[node]
# Create a clone for the given node.
# Note that we don't have cloned neighbors as of now, hence [].
clone_node = Node(node.val, [])
# The key is original node and value being the clone node.
self.visited[node] = clone_node
# Iterate through the neighbors to generate their clones
# and prepare a list of cloned neighbors to be added to the cloned node.
if node.neighbors:
clone_node.neighbors = [self.cloneGraph(n) for n in node.neighbors]
return clone_node
Approach 2: Breadth First Search
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, neighbors):
self.val = val
self.neighbors = neighbors
"""
from collections import deque
class Solution(object):
def cloneGraph(self, node):
"""
:type node: Node
:rtype: Node
"""
if not node:
return node
# Dictionary to save the visited node and it's respective clone
# as key and value respectively. This helps to avoid cycles.
visited = {}
# Put the first node in the queue
queue = deque([node])
# Clone the node and put it in the visited dictionary.
visited[node] = Node(node.val, [])
# Start BFS traversal
while queue:
# Pop a node say "n" from the from the front of the queue.
n = queue.popleft()
# Iterate through all the neighbors of the node
for neighbor in n.neighbors:
if neighbor not in visited:
# Clone the neighbor and put in the visited, if not present already
visited[neighbor] = Node(neighbor.val, [])
# Add the newly encountered node to the queue.
queue.append(neighbor)
# Add the clone of the neighbor to the neighbors of the clone node "n".
visited[n].neighbors.append(visited[neighbor])
# Return the clone of the node from visited.
return visited[node]