Problem of The Day: Balance a Binary Search Tree
Problem Statement
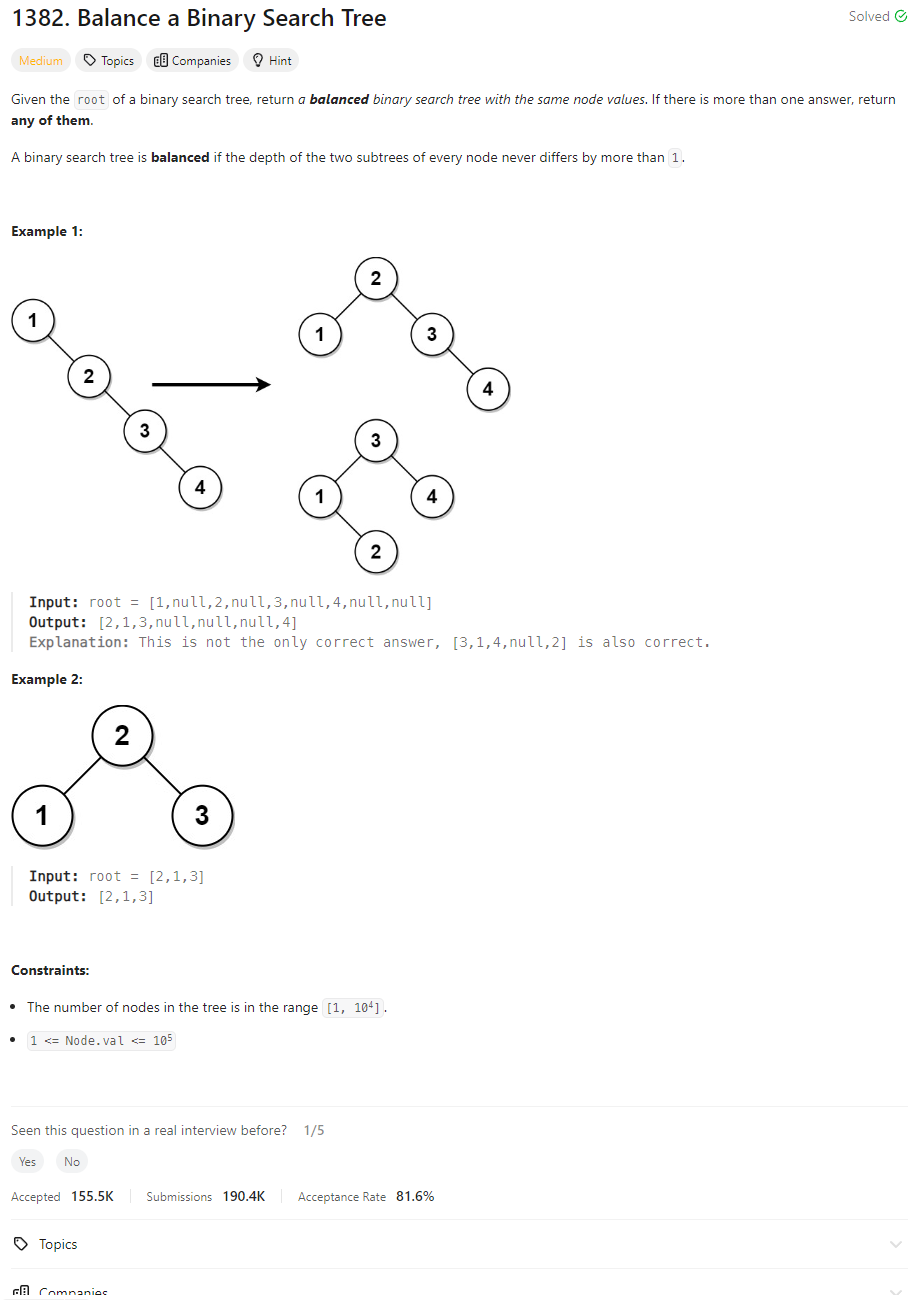
Intuition
My initial thought is to convert the given binary search tree (BST) into a balanced BST. To achieve this, the tree needs to be restructured so that the heights of the two subtrees of any node differ by no more than one.
Approach
First, I will perform an in-order traversal of the given BST. This will give me a sorted list of the tree’s nodes. Once I have this sorted list, I can use it to construct a balanced BST by recursively choosing the middle element of the list (or sublist) as the root of the tree (or subtree). This ensures that the tree is balanced because each subtree will be approximately the same size.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(n)
-
Space complexity: O(n)
Code
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def balanceBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
sorted_list = []
def inorder(node):
if not node:
return
inorder(node.left)
sorted_list.append(node)
inorder(node.right)
def helper(sorted_list, l, r):
if l > r:
return
m = l + (r - l) // 2
node = sorted_list[m]
node.left = helper(sorted_list, l, m - 1)
node.right = helper(sorted_list, m + 1, r)
return node
inorder(root)
l, r = 0, len(sorted_list) - 1
return helper(sorted_list, l, r)
Editorial
class Solution:
def balanceBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
# Create a list to store the inorder traversal of the BST
inorder = []
self.inorder_traversal(root, inorder)
# Construct and return the balanced BST
return self.create_balanced_bst(inorder, 0, len(inorder) - 1)
def inorder_traversal(self, root: TreeNode, inorder: list):
# Perform an inorder traversal to store the elements in sorted order
if not root:
return
self.inorder_traversal(root.left, inorder)
inorder.append(root.val)
self.inorder_traversal(root.right, inorder)
def create_balanced_bst(
self, inorder: list, start: int, end: int
) -> TreeNode:
# Base case: if the start index is greater than the end index, return None
if start > end:
return None
# Find the middle element of the current range
mid = start + (end - start) // 2
# Recursively construct the left and right subtrees
left_subtree = self.create_balanced_bst(inorder, start, mid - 1)
right_subtree = self.create_balanced_bst(inorder, mid + 1, end)
# Create a new node with the middle element and attach the subtrees
node = TreeNode(inorder[mid], left_subtree, right_subtree)
return node