Problem of The Day: Water Bottles
Problem Statement
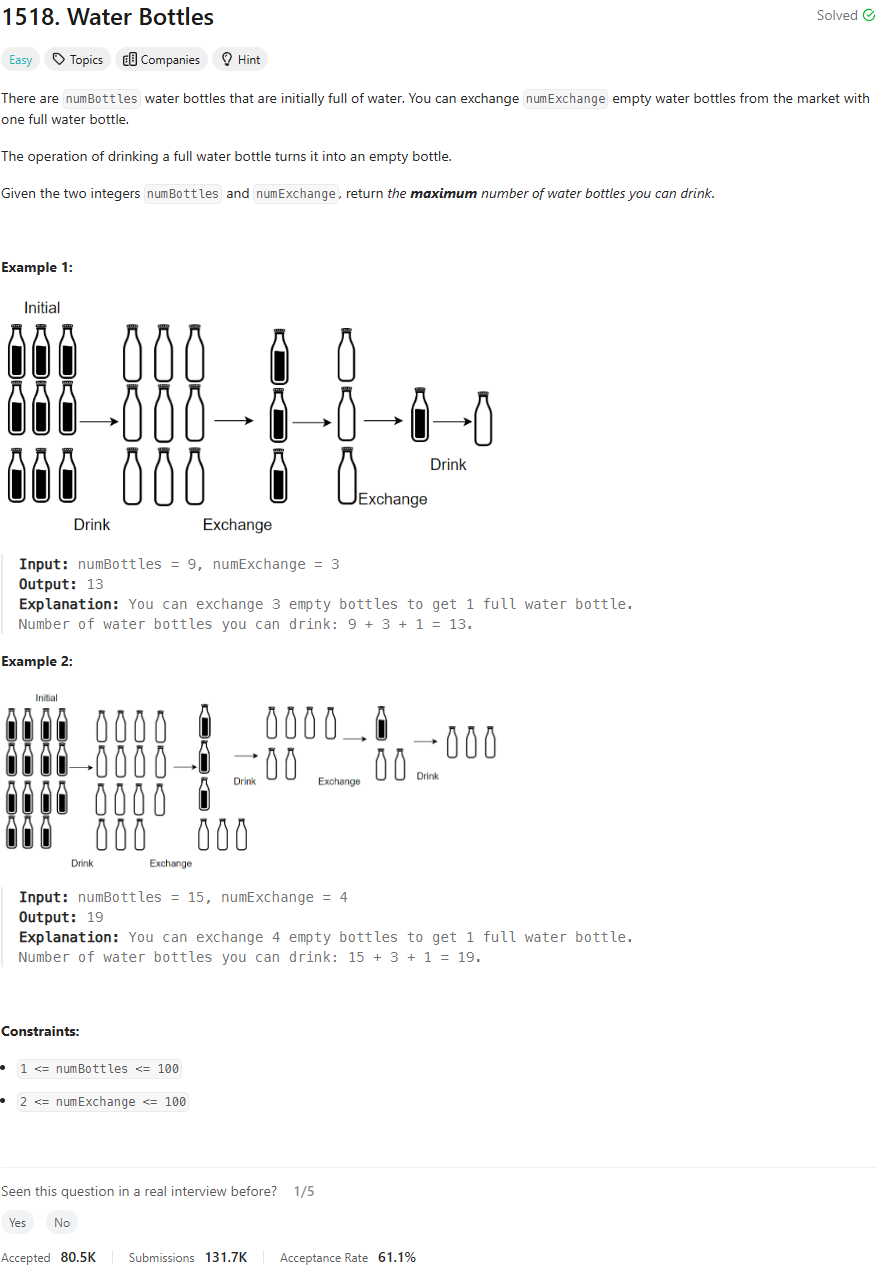
Intuition
My first thought on solving this problem is to simulate the process of drinking and exchanging water bottles. The key is to keep track of the number of full bottles we have, the number of empty bottles we accumulate, and how we can exchange these empty bottles for new full ones. By doing this, I can determine the total number of bottles we can drink.
Approach
- Initialize
reswith the initial number of water bottles (numBottles) as we can drink all of these. - Use a while loop to continue the process as long as we have enough empty bottles to exchange for at least one full bottle (
numBottles >= numExchange). - In each iteration:
- Calculate the remaining empty bottles after the exchange using the modulus operation (
emptyBottles = numBottles % numExchange). - Determine the number of new full bottles we get from exchanging the empty ones (
numBottles = numBottles // numExchange). - Add the newly obtained full bottles to the total count (
res += numBottles). - Update the number of full bottles by adding the remaining empty bottles (
numBottles += emptyBottles).
- Calculate the remaining empty bottles after the exchange using the modulus operation (
- Continue this process until we can no longer exchange empty bottles for full ones.
- Return the total count of water bottles consumed.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: The time complexity is \(O(\log_{numExchange}(numBottles))\) because in each iteration, the number of full bottles is reduced by a factor related to
numExchange. -
Space complexity: The space complexity is \(O(1)\) as we are using a constant amount of extra space.
Code
class Solution:
def numWaterBottles(self, numBottles: int, numExchange: int) -> int:
res = numBottles
emptyBottles = 0
while numBottles >= numExchange:
emptyBottles = numBottles % numExchange
numBottles = numBottles // numExchange
res += numBottles
numBottles += emptyBottles
return res
Editorial
Approach 1: Simulation
class Solution:
def numWaterBottles(self, numBottles: int, numExchange: int) -> int:
consumed_bottles = 0
while numBottles >= numExchange:
# Consume numExchange full bottles.
consumed_bottles += numExchange
numBottles -= numExchange
# Exchange them for one full bottle.
numBottles += 1
# Consume the remaining numBottles (less than numExchange).
return consumed_bottles + numBottles
- time: O(n)
- space: O(1)
Approach 2: Optimized Simulation
class Solution:
def numWaterBottles(self, numBottles: int, numExchange: int) -> int:
consumed_bottles = 0
while numBottles >= numExchange:
# Maximum number of times we can consume numExchange
# number of bottles using numBottles.
K = numBottles // numExchange
consumed_bottles += numExchange * K
numBottles -= numExchange * K
numBottles += K
return consumed_bottles + numBottles
- time: \(O(\log_{numExchange}(numBottles))\), hence O(log N) where N is the number of initial full bottles.
- space: O(1)