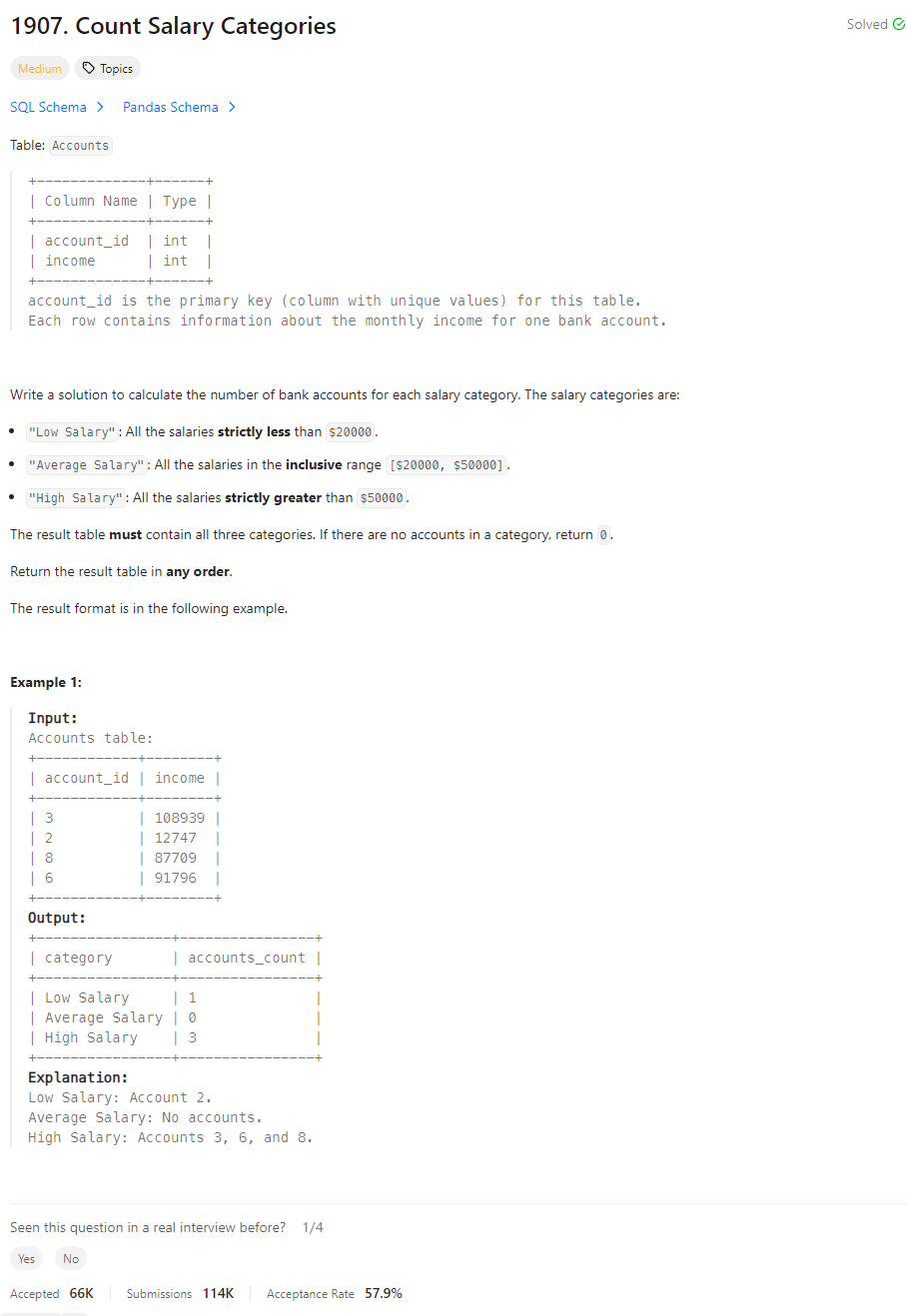
SQL problem - Count Salary Categories
Problem
Note:
The main difference between UNION vs UNION ALL is their approach to duplicate rows. After UNION combines datasets, it also checks for duplicate records and removes them. UNION ALL only combines them and stops there.
Query
(
SELECT "Low Salary" as category, COUNT(income) AS accounts_count
FROM Accounts
WHERE income < 20000
)
UNION ALL
(
SELECT "Average Salary" as category, COUNT(income) AS accounts_count
FROM Accounts
WHERE income BETWEEN 20000 AND 50000
)
UNION ALL
(
SELECT "High Salary" as category, COUNT(income) AS accounts_count
FROM Accounts
WHERE income > 50000
)
Editorial Solution
SELECT
'Low Salary' AS category,
SUM(CASE WHEN income < 20000 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS accounts_count
FROM
Accounts
UNION
SELECT
'Average Salary' category,
SUM(CASE WHEN income >= 20000 AND income <= 50000 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END)
AS accounts_count
FROM
Accounts
UNION
SELECT
'High Salary' category,
SUM(CASE WHEN income > 50000 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS accounts_count
FROM
Accounts