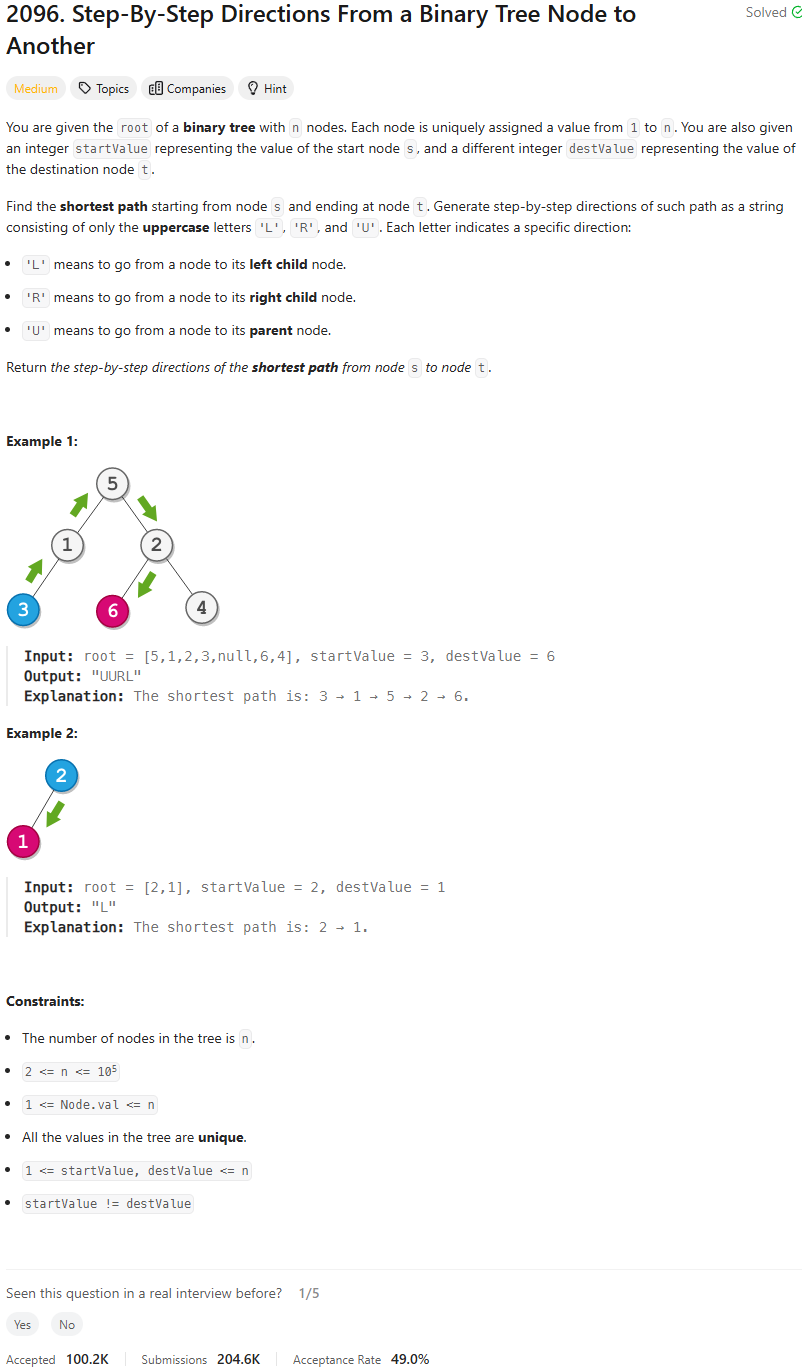
Problem of The Day: Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another
Problem Statement
Brute Force - MLE
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def getDirections(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], startValue: int, destValue: int) -> str:
curr = []
res = []
def findStartNode(node, stack):
if not node:
return
if node.val == startValue:
stack.append(node)
return stack
return findStartNode(node.left, stack + [node]) or findStartNode(node.right, stack + [node])
def search(node, curr):
if not node:
return False
if node.val == destValue:
return curr
return search(node.left, curr + ['L']) or search(node.right, curr + ['R'])
stack = findStartNode(root, [])
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
res = search(node, curr)
if res:
return ''.join(res)
curr.append('U')
Attempted to solve using the LCA problem, but still get MLE
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def getDirections(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], startValue: int, destValue: int) -> str:
self.lca = root.val
def findLCA(node):
if not node:
return False
L = findLCA(node.left)
R = findLCA(node.right)
startNode = node.val == startValue
destNode = node.val == destValue
if L + R + startNode + destNode >= 2:
self.lca = node.val
return True
return L or R or startNode or destNode
def helper(node, target, curr):
if not node:
return
if node.val == target:
return curr
return helper(node.left, target, curr + [(node.val, 'L')]) \
or helper(node.right, target, curr + [(node.val, 'R')])
l1 = helper(root, startValue, [])
l2 = helper(root, destValue, [])
findLCA(root)
idx = 0
res = []
for i in range(max(len(l1), len(l2))):
node1, _ = l1[i] if i < len(l1) else l2[i]
node2, _ = l2[i] if i < len(l2) else l1[i]
if node1 == self.lca or node2 == self.lca:
idx = i
break
j = k = idx
while j < len(l1):
res.append('U')
j += 1
while k < len(l2):
res.append(l2[k][1])
k += 1
return ''.join(res)
Problem with the above solutions is in the helper function. If we replace it with the following function from Editorial solution. The submission is accepted.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def getDirections(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], startValue: int, destValue: int) -> str:
self.lca = root
def findLCA(node):
if not node:
return False
L = findLCA(node.left)
R = findLCA(node.right)
startNode = node.val == startValue
destNode = node.val == destValue
if L + R + startNode + destNode >= 2:
self.lca = node
return True
return L or R or startNode or destNode
def helper(node, target_value, path):
if node is None:
return False
if node.val == target_value:
return True
# Try left subtree
path.append("L")
if helper(node.left, target_value, path):
return True
path.pop() # Remove last character
# Try right subtree
path.append("R")
if helper(node.right, target_value, path):
return True
path.pop() # Remove last character
return False
findLCA(root)
l1 = []
l2 = []
helper(self.lca, startValue, l1)
helper(self.lca, destValue, l2)
res = []
res.extend('U' * len(l1))
res.extend(l2)
return ''.join(res)
Editorial
class Solution:
def getDirections(
self, root: TreeNode, startValue: int, destValue: int
) -> str:
# Find the Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA) of start and destination nodes
lowest_common_ancestor = self._find_lowest_common_ancestor(
root, startValue, destValue
)
path_to_start = []
path_to_dest = []
# Find paths from LCA to start and destination nodes
self._find_path(lowest_common_ancestor, startValue, path_to_start)
self._find_path(lowest_common_ancestor, destValue, path_to_dest)
directions = []
# Add "U" for each step to go up from start to LCA
directions.extend("U" * len(path_to_start))
# Append the path from LCA to destination
directions.extend(path_to_dest)
return "".join(directions)
def _find_lowest_common_ancestor(
self, node: TreeNode, value1: int, value2: int
) -> TreeNode:
if node is None:
return None
if node.val == value1 or node.val == value2:
return node
left_lca = self._find_lowest_common_ancestor(node.left, value1, value2)
right_lca = self._find_lowest_common_ancestor(
node.right, value1, value2
)
if left_lca is None:
return right_lca
elif right_lca is None:
return left_lca
else:
return node # Both values found, this is the LCA
def _find_path(
self, node: TreeNode, target_value: int, path: List[str]
) -> bool:
if node is None:
return False
if node.val == target_value:
return True
# Try left subtree
path.append("L")
if self._find_path(node.left, target_value, path):
return True
path.pop() # Remove last character
# Try right subtree
path.append("R")
if self._find_path(node.right, target_value, path):
return True
path.pop() # Remove last character
return False