Problem of The Day: Double a Number Represented as a Linked List
Problem Statement
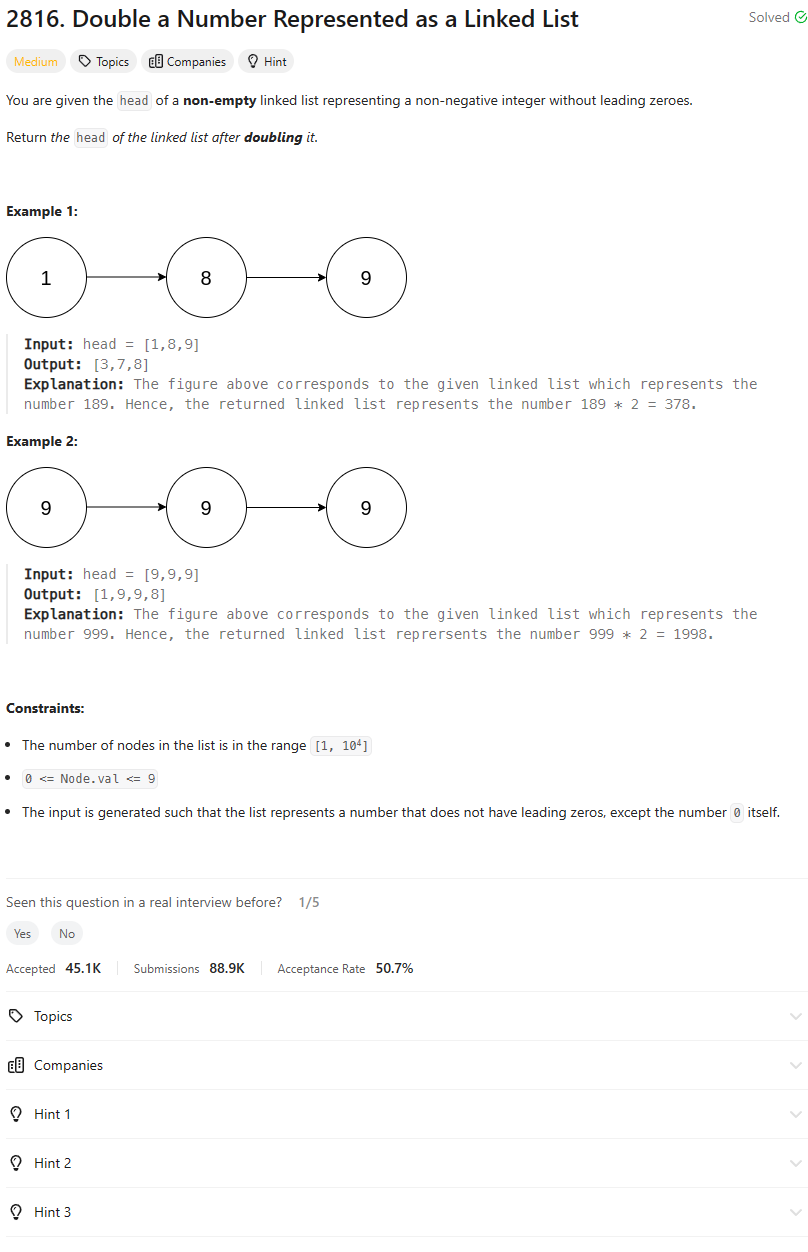
Intuition
The problem seems to involve traversing a singly-linked list and doubling each digit, considering any carryover. A recursive approach might be suitable for this task.
Approach
Define a helper function to recursively traverse the linked list, starting from the last node. Within this function, update each node’s value by doubling it and considering any carryover from the previous node. If there’s a carryover after the traversal, prepend a new node with the carryover value to the linked list.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(n) where n is the number of nodes in the linked list
-
Space complexity: O(n)
Code
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def doubleIt(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
def helper(node):
if not node:
return 0
carry = helper(node.next)
carry += node.val * 2
node.val = carry % 10
return carry // 10
carry = helper(head)
if carry == 1:
return ListNode(carry, head)
return head
Editorial Solution
Approach 1: Reversing the List
class Solution:
def doubleIt(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# Reverse the linked list
reversed_list = self.reverse_list(head)
# Initialize variables to track carry and previous node
carry = 0
current, previous = reversed_list, None
# Traverse the reversed linked list
while current:
# Calculate the new value for the current node
new_value = current.val * 2 + carry
# Update the current node's value
current.val = new_value % 10
# Update carry for the next iteration
carry = 1 if new_value > 9 else 0
# Move to the next node
previous, current = current, current.next
# If there's a carry after the loop, add an extra node
if carry:
previous.next = ListNode(carry)
# Reverse the list again to get the original order
result = self.reverse_list(reversed_list)
return result
# Method to reverse the linked list
def reverse_list(self, node: ListNode) -> ListNode:
previous, current = None, node
# Traverse the original linked list
while current:
# Store the next node
next_node = current.next
# Reverse the link
current.next = previous
# Move to the next nodes
previous, current = current, next_node
# Previous becomes the new head of the reversed list
return previous
- Time: O(n)
- Space: O(1)
Approach 2: Using Stack
class Solution:
# To compute twice the value of each node's value and propagate carry
def twice_of_val(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> int:
# Base case: if head is None, return 0
if not head:
return 0
# Double the value of current node and add the result of next nodes
doubled_value = head.val * 2 + self.twice_of_val(head.next)
# Update current node's value with the units digit of the result
head.val = doubled_value % 10
# Return the carry (tens digit of the result)
return doubled_value // 10
def doubleIt(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
carry = self.twice_of_val(head)
# If there's a carry, insert a new node at the beginning with the carry value
if carry:
head = ListNode(carry, head)
# Return the head of the updated linked list
return head
### class Solution:
# To compute twice the value of each node's value and propagate carry
def twice_of_val(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> int:
# Base case: if head is None, return 0
if not head:
return 0
# Double the value of current node and add the result of next nodes
doubled_value = head.val * 2 + self.twice_of_val(head.next)
# Update current node's value with the units digit of the result
head.val = doubled_value % 10
# Return the carry (tens digit of the result)
return doubled_value // 10
def doubleIt(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
carry = self.twice_of_val(head)
# If there's a carry, insert a new node at the beginning with the carry value
if carry:
head = ListNode(carry, head)
# Return the head of the updated linked list
return head
Approach 4: Two Pointers
class Solution:
def doubleIt(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
curr = head
prev = None
# Traverse the linked list
while curr:
twice_of_val = curr.val * 2
# If the doubled value is less than 10
if twice_of_val < 10:
curr.val = twice_of_val
# If doubled value is 10 or greater
elif prev: # other than first node
# Update current node's value with units digit of the doubled value
curr.val = twice_of_val % 10
# Add the carry to the previous node's value
prev.val += 1
else: # first node
# Create a new node with carry as value and link it to the current node
head = ListNode(1, curr)
# Update current node's value with units digit of the doubled value
curr.val = twice_of_val % 10
# Update prev and curr pointers
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
return head