Problem of The Day: String Compression III
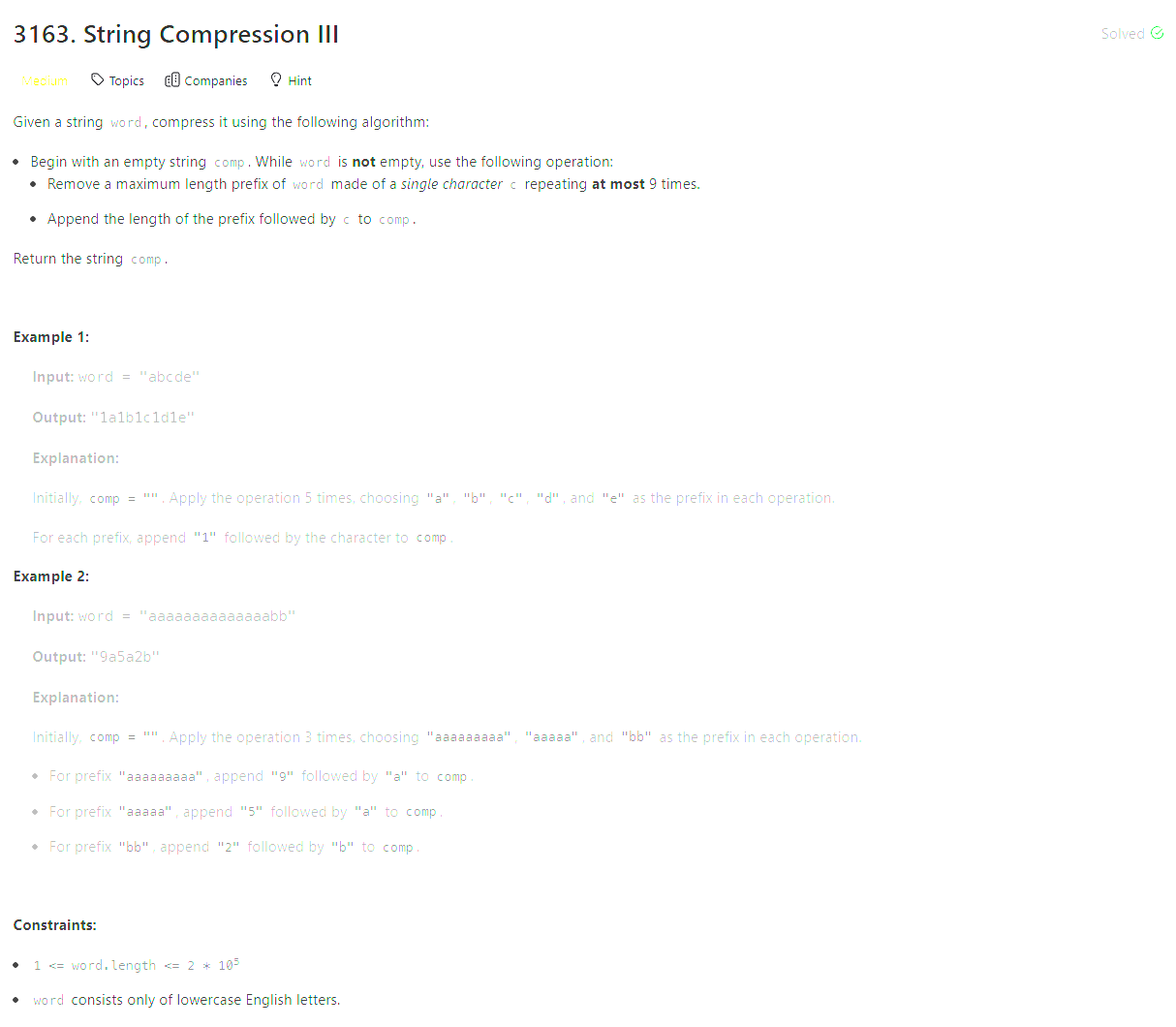
Problem Statement
Intuition
The initial idea was to compress a string by grouping consecutive identical characters and keeping track of their frequency. By replacing consecutive characters with a count followed by the character itself, we reduce the string length, especially when there are long sequences of the same character. This approach seemed efficient for generating a compressed string without performing multiple scans or transformations.
Approach
- Initialize a Queue: Use a queue to store pairs of characters and their consecutive counts as we iterate through the string.
- Iterate Through Each Character:
- For each character
cin the input stringword, check the last character stored in the queue. - If the queue is empty, add the character
cwith a count of 1. - If
cmatches the last character in the queue and its frequency is less than 9 (to avoid exceeding a single-digit limit), increment the frequency of the last character in the queue. - Otherwise, push
cto the queue with a frequency of 1.
- For each character
- Build the Result:
- Once all characters are processed, use a loop to dequeue elements from
queue. - Append each character’s frequency and value to a result list,
res.
- Once all characters are processed, use a loop to dequeue elements from
- Return the Compressed String:
- Join the elements in
resto form the final compressed string.
- Join the elements in
Complexity
- Time complexity: \(O(n)\) where ( n ) is the length of
word, as we perform a single pass through the input string. - Space complexity: \(O(n)\), due to the queue and result list used to store intermediate values.
Code
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def compressedString(self, word: str) -> str:
queue = deque()
res = []
for c in word:
if not queue:
queue.append([c, 1])
else:
if c == queue[-1][0] and queue[-1][1] < 9:
queue[-1][1] += 1
else:
queue.append([c, 1])
while queue:
c, f = queue.popleft()
res.append(str(f) + c)
return ''.join(res)
Editorial
Approach: String Manipulation
class Solution:
def compressedString(self, word: str) -> str:
comp = []
# pos tracks our position in the input string
pos = 0
# Process until we reach end of string
while pos < len(word):
consecutive_count = 0
current_char = word[pos]
# Count consecutive occurrences (maximum 9)
while (
pos < len(word)
and consecutive_count < 9
and word[pos] == current_char
):
consecutive_count += 1
pos += 1
# Append count followed by character to the list
comp.append(str(consecutive_count))
comp.append(current_char)
# Join the list into a single string for the final result
return "".join(comp)
- time: O(n)
- space: O(1)