Problem of The Day:Minimum Genetic Mutation
Problem Statement

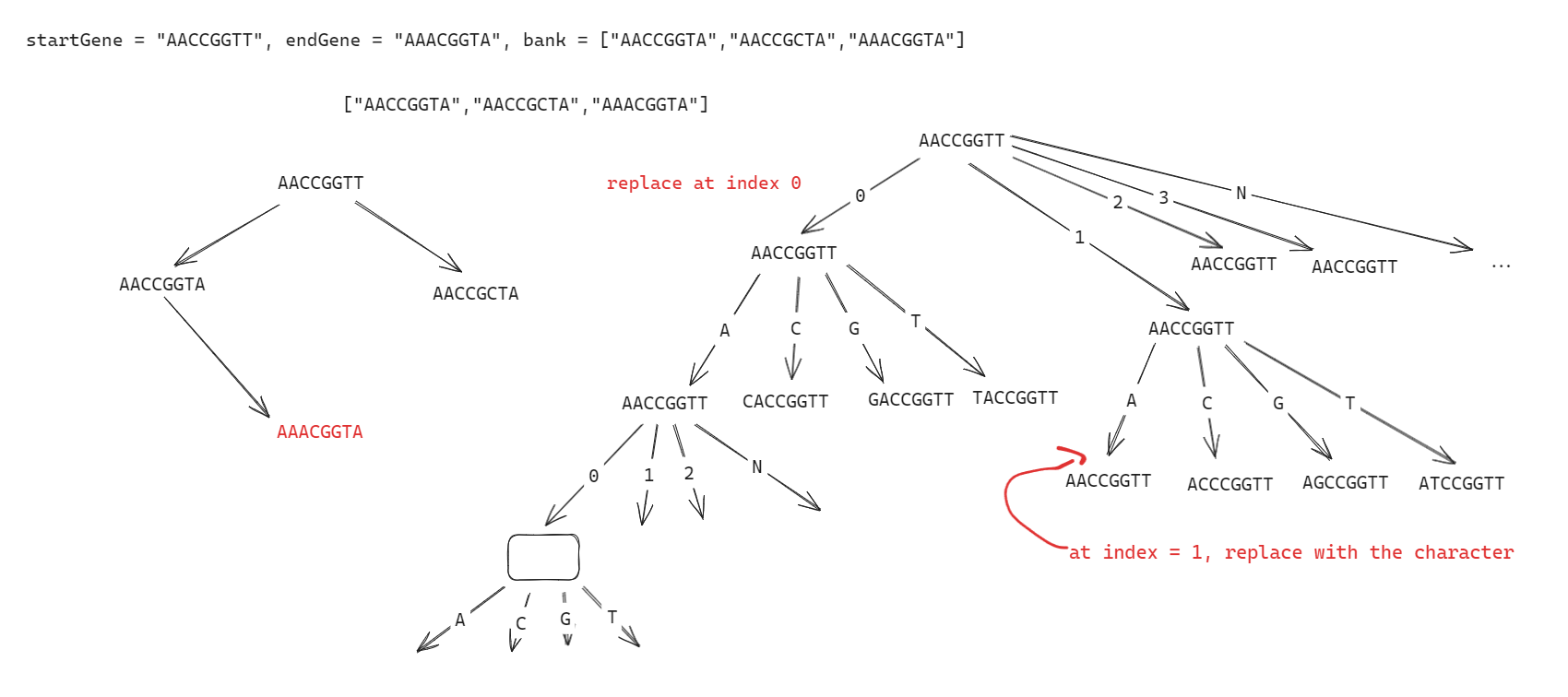
My notes:
Intuition
Upon examining the problem, my initial thought was to use a breadth-first search (BFS) approach since we need to find the shortest mutation path from the start gene to the end gene.
Approach
My approach involves utilizing a queue to perform BFS. Starting from the start gene, I generate all possible mutations by replacing each character with ‘A’, ‘C’, ‘G’, and ‘T’ iteratively. For each mutation, I check if it matches the end gene. If it does, and it’s in the bank, we return the number of mutations. Otherwise, we continue exploring mutations until we find the end gene or exhaust all possibilities.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: Let N be the length of the start gene. Generating each mutation takes O(N) time, and since we explore each mutation once, the overall time complexity is O(N * 4^N), where 4^N represents the number of possible mutations.
-
Space complexity: The space complexity is determined by the queue and the visited set. In the worst case, where all possible mutations are explored, the space complexity is O(4^N) due to the queue. Additionally, the visited set may contain up to O(4^N) elements. Thus, the overall space complexity is O(4^N).
Code
class Solution:
def minMutation(self, startGene: str, endGene: str, bank: List[str]) -> int:
queue = deque()
queue.append([startGene, 0])
visited = set()
N = len(startGene)
while queue:
node, mutations = queue.popleft()
for i in range(N):
gene_str_list = list(node)
for c in ['A', 'C', 'G', 'T']:
if c != gene_str_list[i]:
gene_str_list[i] = c
new_gene = ''.join(gene_str_list)
if new_gene == endGene and new_gene in bank:
return mutations + 1
if new_gene not in visited:
if new_gene in bank:
visited.add(new_gene)
queue.append([new_gene, mutations + 1])
return -1
Editorial Solution
Approach: BFS (Breadth-First Search)
class Solution:
def minMutation(self, start: str, end: str, bank: List[str]) -> int:
queue = deque([(start, 0)])
seen = {start}
while queue:
node, steps = queue.popleft()
if node == end:
return steps
for c in "ACGT":
for i in range(len(node)):
neighbor = node[:i] + c + node[i + 1:]
if neighbor not in seen and neighbor in bank:
queue.append((neighbor, steps + 1))
seen.add(neighbor)
return -1