Problem of The Day: Diagonal Traverse
Problem Statement
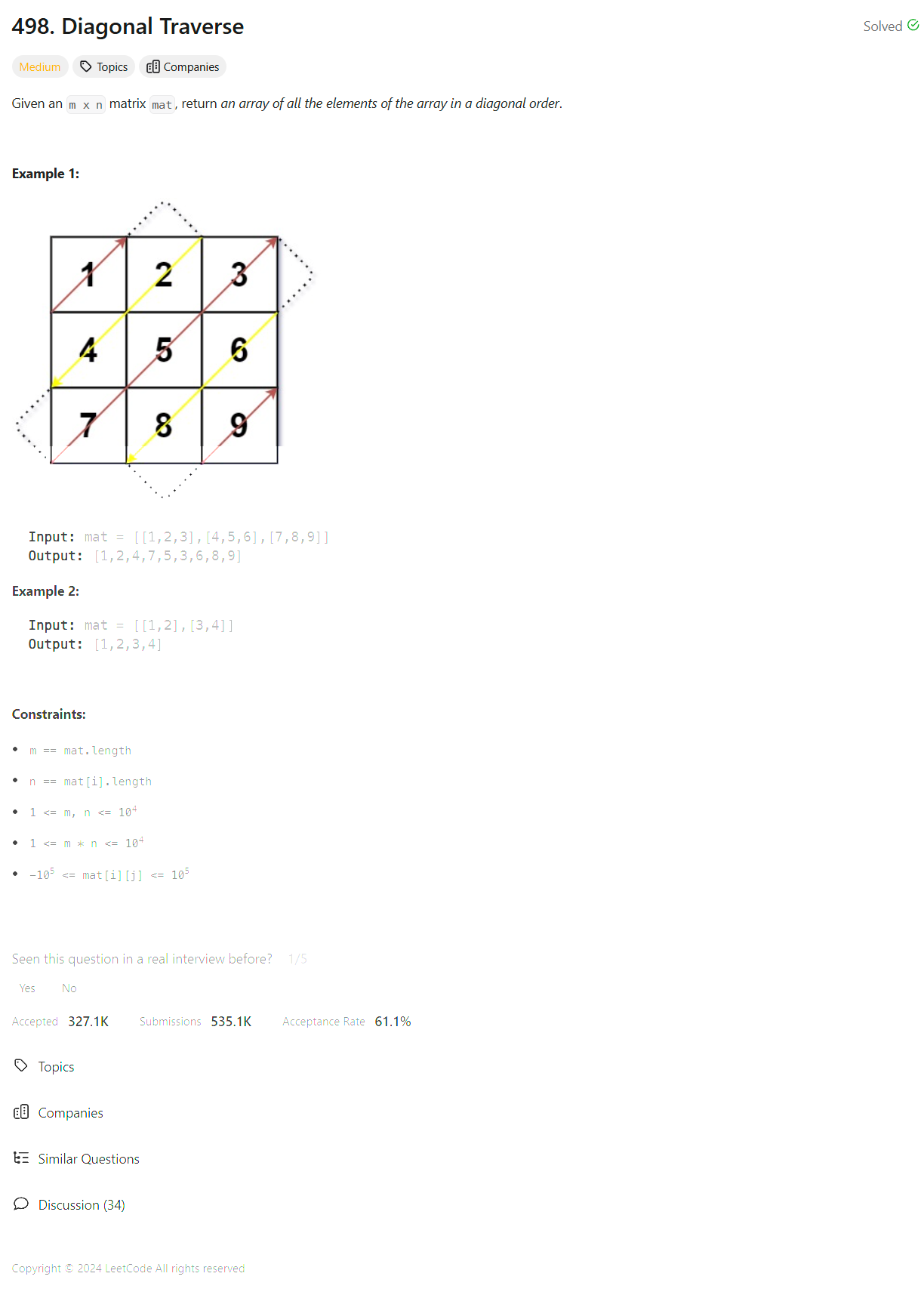
Approach
We traverse the matrix diagonally, extracting each diagonal in two phases:
- First, starting from each row in the first column.
- Second, starting from each column in the last row.
For each diagonal, we determine whether to reverse it based on whether we’re moving bottom-to-top or top-to-bottom. We then append the results of each diagonal traversal to our output list.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: Since we’re traversing the entire matrix and each element is processed exactly once, the time complexity is \(O(n)\), where n is the total number of elements in the matrix (i.e., rows * columns).
-
Space complexity: The space complexity is \(O(n)\), where n is the total number of elements stored in the resulting list.
Code
class Solution:
def findDiagonalOrder(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
ROWS = len(mat)
COLS = len(mat[0])
N = ROWS * COLS
res = []
bottom_to_top = True
for row in range(ROWS):
curr = []
r, c = row, 0
while r >= 0 and c < COLS:
curr.append(mat[r][c])
r -= 1
c += 1
if not bottom_to_top:
curr = curr[::-1]
res.extend(curr)
bottom_to_top = not bottom_to_top
for col in range(1, COLS):
curr = []
r, c = ROWS - 1, col
while r >= 0 and c < COLS:
curr.append(mat[r][c])
r -= 1
c += 1
if not bottom_to_top:
curr = curr[::-1]
res.extend(curr)
bottom_to_top = not bottom_to_top
return res
Discussion Solution
class Solution:
def findDiagonalOrder(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
up = True
i = 0
j = 0
m = len(mat)
n = len(mat[0])
o = []
while len(o) < m * n: # Continue until we've processed all elements
o.append(mat[i][j])
if up:
if i - 1 >= 0 and j + 1 < n: # Move up diagonally
i -= 1
j += 1
else: # Change direction if boundary is hit
up = False
if j + 1 < n: # Move right if possible
j += 1
else: # Else move down
i += 1
else:
if i + 1 < m and j - 1 >= 0: # Move down diagonally
i += 1
j -= 1
else: # Change direction if boundary is hit
up = True
if i + 1 < m: # Move down if possible
i += 1
else: # Else move right
j += 1
return o