Problem of The Day: Remove Nodes From Linked List
Problem Statement
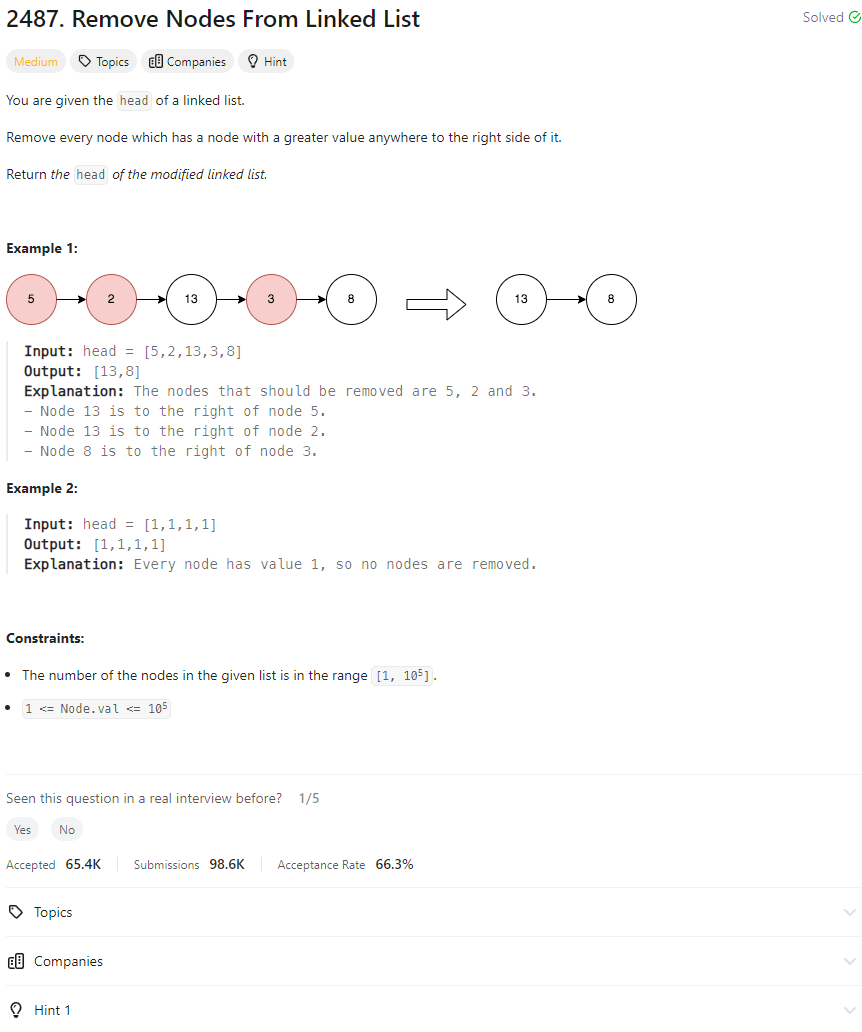
Intuition
Initially, I thought of utilizing a stack to traverse the linked list in reverse order, maintaining a resulting list with nodes that need to be kept based on the condition.
Approach
My approach involves traversing the linked list in reverse order using a stack. I push each node onto the stack, then pop from the stack, adding nodes to the result list if they meet the condition of having a value greater than or equal to the previous node. Finally, I reconstruct the resulting list from the collected nodes.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(n) where n is the number of nodes in the linked list
-
Space complexity: O(n)
Code
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNodes(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head:
return
stack = []
curr = head
while curr:
stack.append(curr)
curr = curr.next
res = []
while stack:
curr = stack.pop()
if not res or curr.val >= res[-1].val:
res.append(curr)
dummy = ListNode(-1)
curr = dummy
while res:
curr.next = res.pop()
curr = curr.next
curr.next = None
return dummy.next
Editorial Solution
Approach 1: Stack
class Solution:
def removeNodes(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
stack = []
current = head
# Add nodes to the stack
while current:
stack.append(current)
current = current.next
current = stack.pop()
maximum = current.val
result_list = ListNode(maximum)
# Remove nodes from the stack and add to result
while stack:
current = stack.pop()
# Current should not be added to the result
if current.val < maximum:
continue
# Add new node with current's value to front of the result
else:
new_node = ListNode(current.val)
new_node.next = result_list
result_list = new_node
maximum = current.val
return result_list
Approach 2: Recursion
class Solution:
def removeNodes(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# Base case, reached end of the list
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
# Recursive call
next_node = self.removeNodes(head.next)
# If the next node has greater value than head, delete the head
# Return next node, which removes the current head and
# makes next the new head
if head.val < next_node.val:
return next_node
# Keep the head
head.next = next_node
return head