Problem of The Day: Reverse Linked List
Problem Statement
See Problem
My note:
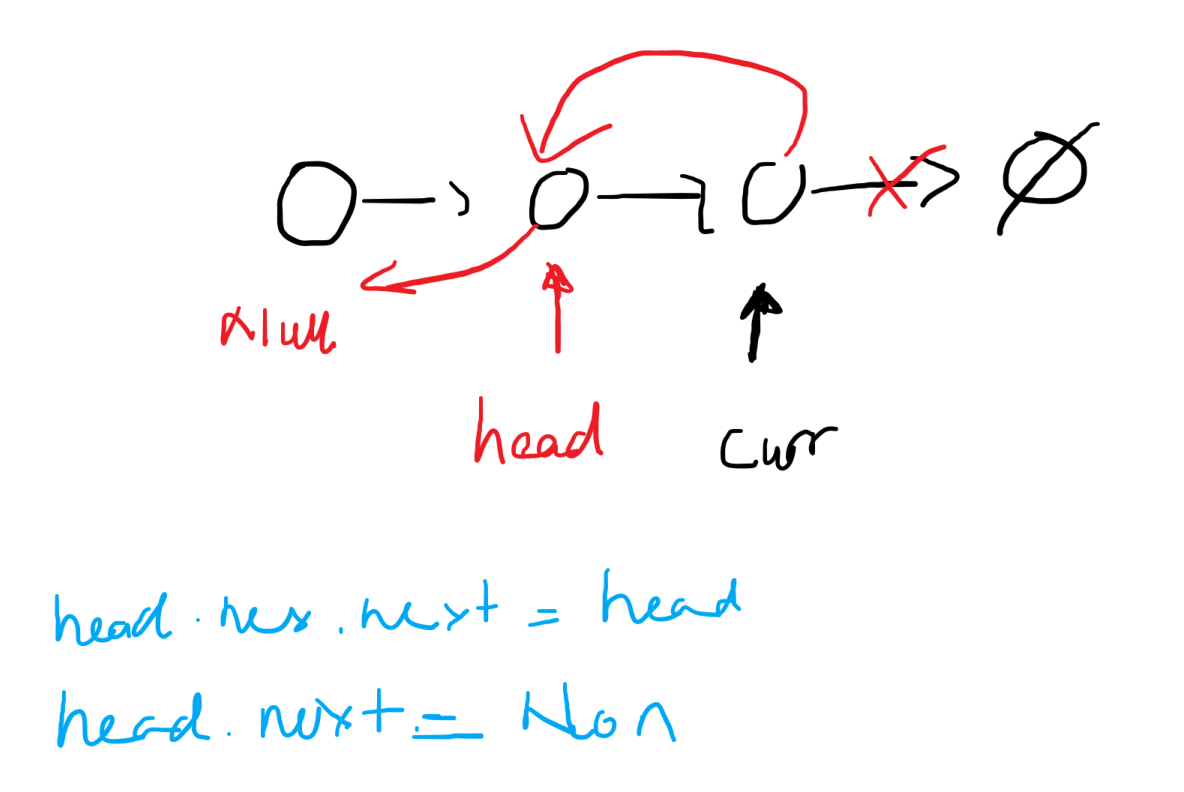
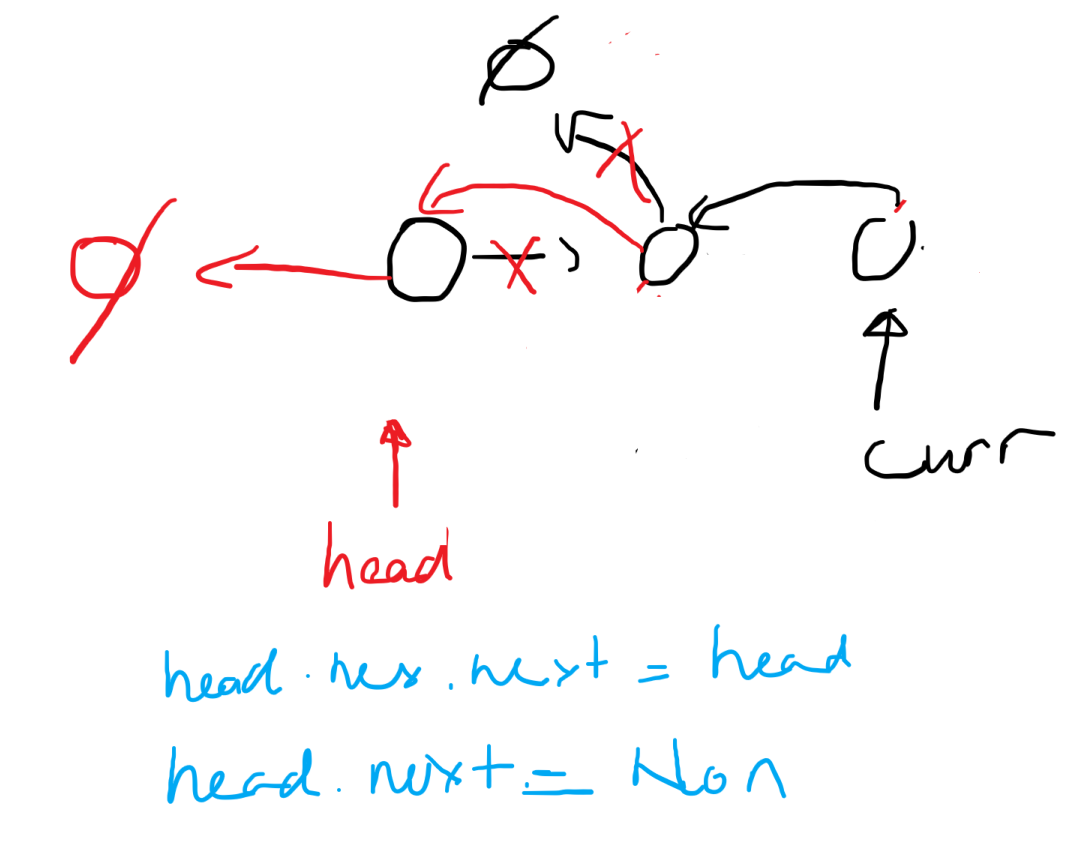
Intuition
Use recursion or stack to do the reverse.
Approach
The function reverseList takes the head of the linked list as an argument. It recursively reverses the remaining portion of the list and adjusts the pointers to reverse the current node. The base cases check if the head is None or if it is the last node, in which case it returns the head.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list. Each node is visited once during the reversal process.
-
Space complexity: O(n), where n is the maximum depth of the recursive call stack. The space required is proportional to the length of the linked list.
Code
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head:
return
if head and not head.next:
return head
curr = self.reverseList(head.next)
head.next.next = head
head.next = None
return curr
Editorial Solution
Iterative Approach
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
prev = None
curr = head
while curr:
next_temp = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next_temp
return prev
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
Recursion Approach
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if (not head) or (not head.next):
return head
p = self.reverseList(head.next)
head.next.next = head
head.next = None
return p
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(n)