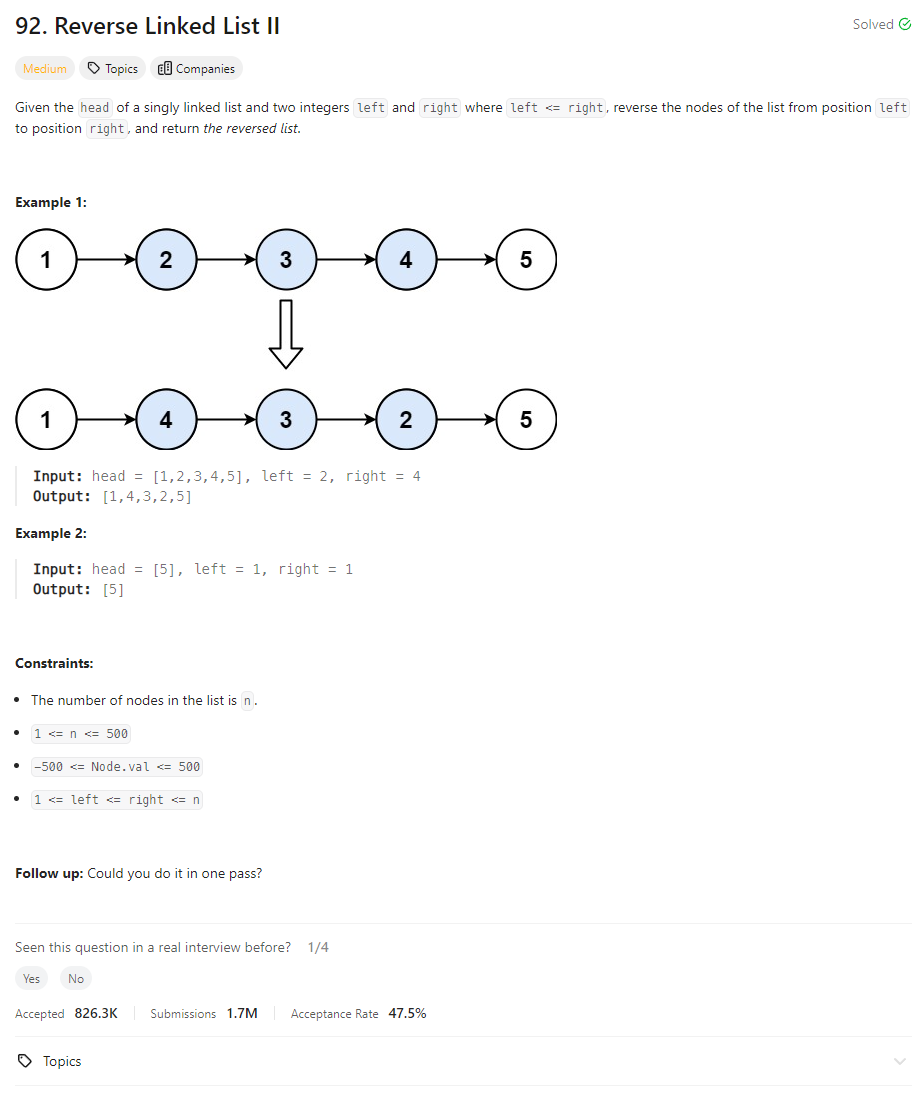
Problem of The Day: Reverse Linked List II
Problem Statement
Intuition
My initial thoughts are to traverse the list until the specified range, reverse that portion, and then connect it back to the original list.
Approach
I will use two pointers, prev and curr, to traverse the linked list until I reach the node at index left. At this point, I’ll start reversing the nodes until I reach the node at index right. I’ll also keep track of the nodes before and after the reversed portion. Finally, I’ll connect these nodes appropriately to ensure the reversed portion is integrated back into the original list.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(n)
-
Space complexity: O(1)
Code
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head: Optional[ListNode], left: int, right: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if left is right:
return head
dummy = ListNode(-1, head)
prev_left = curr = head
left_node = right_node = None
prev = dummy
next_right = None
count = 1
while curr:
if count == left:
left_node = curr
prev_left = prev
if count == right:
right_node = curr
next_right = curr.next
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
count += 1
prev = None
curr = left_node
right_node.next = None
while curr is not None:
next_node = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next_node
prev_left.next, left_node.next = right_node, next_right
return dummy.next
Editorial Solution
Approach 1: Recursion
class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head, m, n):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type m: int
:type n: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not head:
return None
left, right = head, head
stop = False
def recurseAndReverse(right, m, n):
nonlocal left, stop
# base case. Don't proceed any further
if n == 1:
return
# Keep moving the right pointer one step forward until (n == 1)
right = right.next
# Keep moving left pointer to the right until we reach the proper node
# from where the reversal is to start.
if m > 1:
left = left.next
# Recurse with m and n reduced.
recurseAndReverse(right, m - 1, n - 1)
# In case both the pointers cross each other or become equal, we
# stop i.e. don't swap data any further. We are done reversing at this
# point.
if left == right or right.next == left:
stop = True
# Until the boolean stop is false, swap data between the two pointers
if not stop:
left.val, right.val = right.val, left.val
# Move left one step to the right.
# The right pointer moves one step back via backtracking.
left = left.next
recurseAndReverse(right, m, n)
return head
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(n)
Approach 2: Iterative Link Reversal
class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head, m, n):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type m: int
:type n: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
# Empty list
if not head:
return None
# Move the two pointers until they reach the proper starting point
# in the list.
cur, prev = head, None
while m > 1:
prev = cur
cur = cur.next
m, n = m - 1, n - 1
# The two pointers that will fix the final connections.
tail, con = cur, prev
# Iteratively reverse the nodes until n becomes 0.
while n:
third = cur.next
cur.next = prev
prev = cur
cur = third
n -= 1
# Adjust the final connections as explained in the algorithm
if con:
con.next = prev
else:
head = prev
tail.next = cur
return head
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)