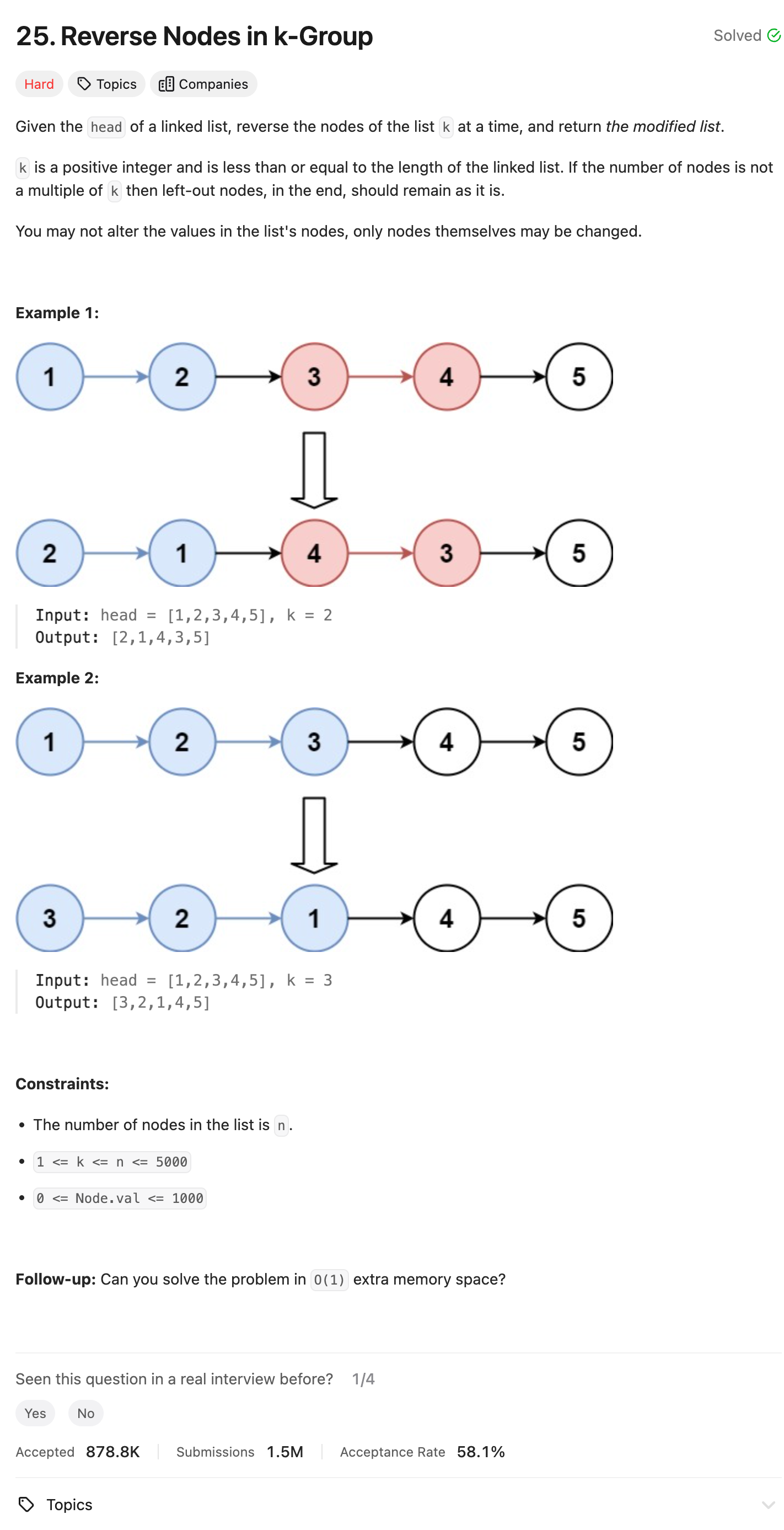
Problem of The Day: Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Problem Statement
My note:
O(n) space Approach (easy)
Stack Implementation - Accepted
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
stack = []
dummy = ListNode(-1)
curr = head
prev = dummy
while curr:
stack.append(curr)
curr = curr.next
if len(stack) == k:
group_prev = prev
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
group_prev.next = node
group_prev = node
group_prev.next = curr
prev = group_prev
return dummy.next
Other Implementation
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
temp = []
curr = head
while curr:
temp.append(curr)
curr = curr.next
for i in range(0, len(temp), k):
l, r = i, i + k - 1
if r >= len(temp):
break
while l < r:
temp[l], temp[r] = temp[r], temp[l]
l += 1
r -= 1
for i in range(len(temp) - 1):
temp[i].next = temp[i + 1]
if temp:
temp[-1].next = None
return temp[0] if temp else None
O(1) space Approach (hard)
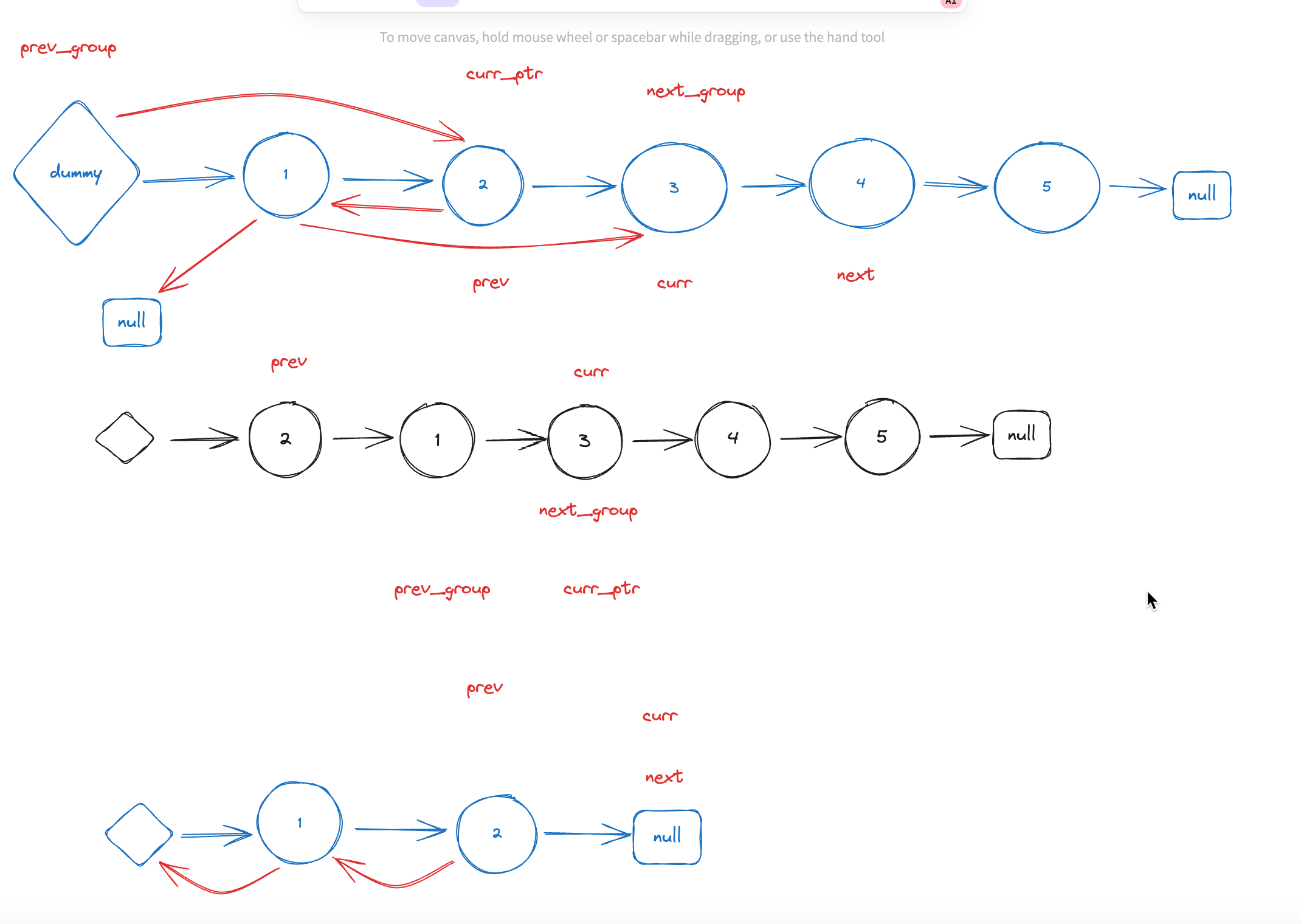
Intuition
The idea is to iterate through the linked list in groups of k nodes, reverse each group, and update the pointers accordingly.
Approach
- Initialize a dummy node to simplify handling edge cases.
- Use two pointers,
prev_groupandcurr_ptr, to keep track of the current group and the current position in the list. - Inside the loop, move
curr_ptrk nodes forward. If there are fewer than k nodes remaining, return the modified list. - Reverse the k nodes in the current group.
- Update pointers to connect the reversed group to the previous and next groups.
- Move
curr_ptrback to the tail of the reversed group to continue the iteration.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list. We process each node once.
-
Space complexity: O(1), as we use a constant amount of extra space regardless of the input size.
Code
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(-1, head)
prev_group = dummy
curr_ptr = dummy
while curr_ptr:
prev_group = curr_ptr
for _ in range(k):
curr_ptr = curr_ptr.next
if not curr_ptr:
return dummy.next
next_group = curr_ptr.next
curr = prev_group.next
tail = curr
prev = None
while curr is not next_group:
next_node = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next_node
prev_group.next = prev
tail.next = next_group
prev_group = tail
curr_ptr = tail
return dummy.next