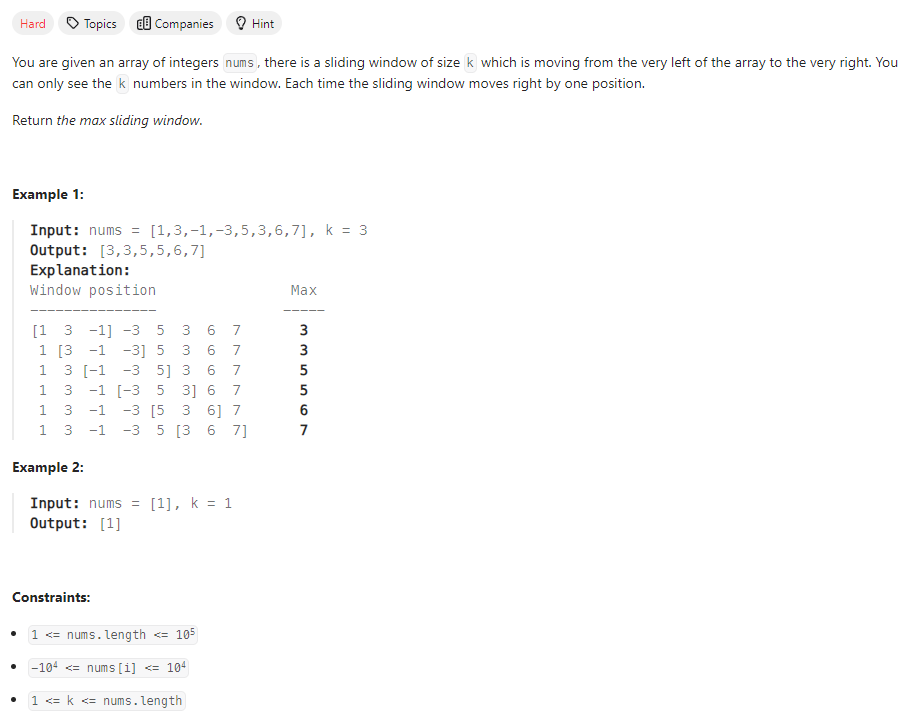
Problem of The Day: Sliding Window Maximum
Problem Statement
Brute Force - Sliding Window - TLE
Intuition
My initial thought is to iterate through the array using a sliding window approach. For each window of size ‘k’, I can find the maximum element and append it to the result list. This approach ensures that we efficiently find the maximum element in each window.
Approach
I will maintain two pointers, ‘start’ and ‘end,’ to represent the sliding window. As I move the window, I’ll check if its size equals ‘k’. If so, I’ll find the maximum element in that window using the ‘max’ function and append it to the result list. Then, I’ll move the window by incrementing the ‘start’ pointer.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(n * k) where ‘n’ is the length of the input array. This is because, for each window of size ‘k’, we are finding the maximum element in that window.
-
Space complexity: O(1) as we are using a constant amount of space for the pointers and the result list.
Code
class Solution:
def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
start = 0
res = []
for end in range(len(nums)):
if end - start + 1 == k:
res.append(max(nums[start:end+1]))
start += 1
return res
Editorial Solution
Approach: Monotonic Deque
The algorithm utilizes a monotonic decreasing queue, implemented as a deque, to efficiently find the maximum element in each sliding window of a given array. It begins by processing the first ‘k’ elements, ensuring that the deque maintains a decreasing order of values. This guarantees that the front of the deque always represents the maximum element in the current window. As the algorithm slides through the array, it adjusts the deque to track the current window, removing indices that are no longer part of the window and eliminating smaller elements from the back. The maximum element in the current window is consistently at the front of the deque, resulting in a streamlined approach to identifying maximum values for each window.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(n)
-
Space complexity: O(k) where k is the size of the deque
Code
class Solution:
def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
dq = deque()
res = []
for i in range(k):
while dq and nums[i] >= nums[dq[-1]]:
dq.pop()
dq.append(i)
res.append(nums[dq[0]])
for i in range(k, len(nums)):
if dq and dq[0] == i - k:
dq.popleft()
while dq and nums[i] >= nums[dq[-1]]:
dq.pop()
dq.append(i)
res.append(nums[dq[0]])
return res