Problem of The Day: Trapping Rain Water
Problem Statement
Intuition
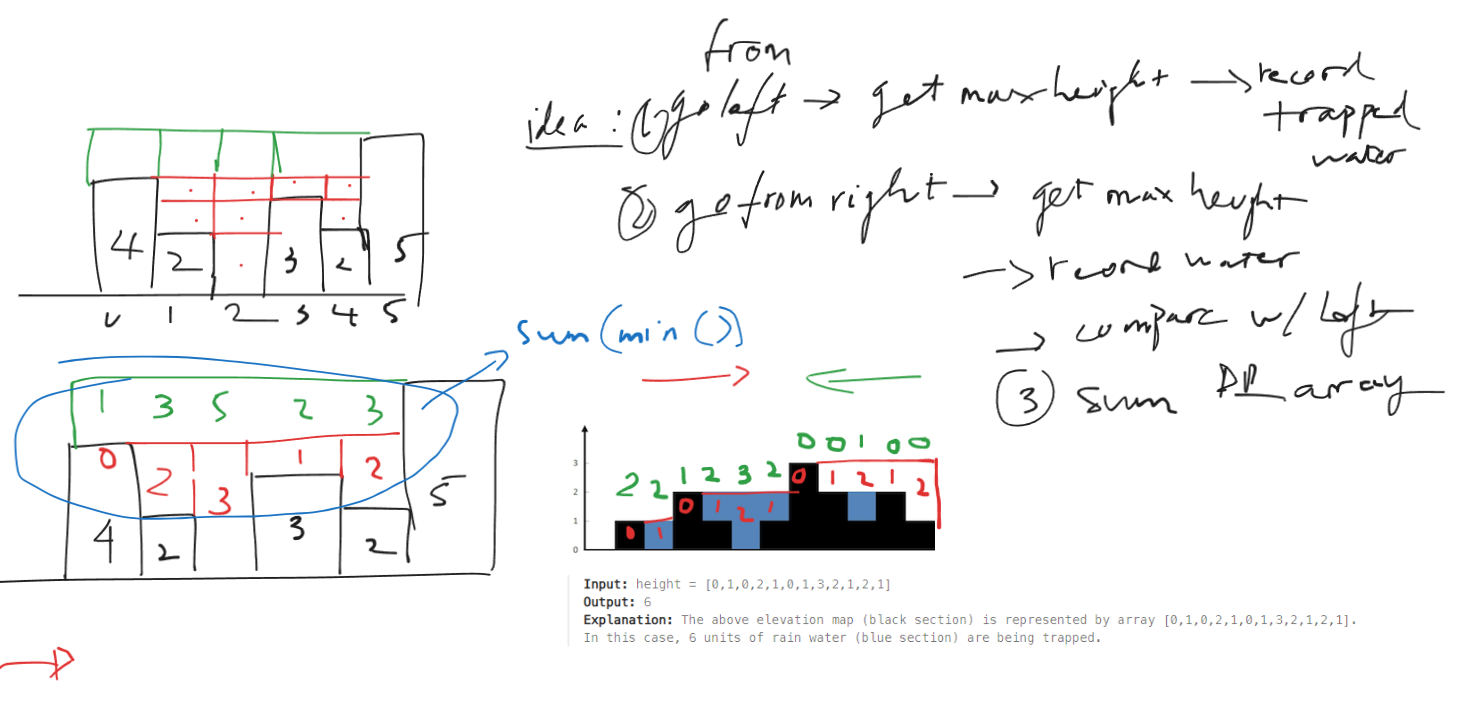
When approaching this problem, I noticed that to calculate the trapped water at each position, it’s essential to understand the elevation of the terrain. The trapped water at any given point depends on the difference between the current height and the maximum height encountered so far.
Approach
To implement my solution, I chose a two-pass approach. In the first pass, I moved from left to right through the elevation map. For each position, I calculated the maximum height encountered so far and stored the difference between this maximum height and the current height in an array called “water.”
In the second pass, I traversed the elevation map in reverse, from right to left. Again, I calculated the maximum height encountered so far, and this time, I updated the trapped water at each position. The trapped water at any point is now the minimum of the previously calculated value and the difference between the current maximum height and the current height.
Finally, I summed up all the values in the “water” array, representing the total trapped water in the elevation map.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(n) linear time, two passes
-
Space complexity: O(n) since I have to keep track of the trapped water in an array.
Code
class Solution:
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
N = len(height)
curr_max = 0
water = [0] * len(height)
for i in range(N):
curr_max = max(curr_max, height[i])
water[i] = curr_max - height[i]
curr_max = 0
for j in reversed(range(N)):
curr_max = max(curr_max, height[j])
water[j] = min(water[j], curr_max - height[j])
return sum(water)
Two pointers Approach
class Solution:
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
l,r = 0,len(height)-1
ans = 0
leftmx, rightmx = 0,0
while l<r:
if height[l]<height[r]:
if height[l]>leftmx:
leftmx= height[l]
else:
ans+= (leftmx-height[l])
l+=1
else:
if height[r]>rightmx:
rightmx= height[r]
else:
ans+= (rightmx-height[r])
r-=1
return ans
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)