Problem of The Day: Zigzag Conversion
Problem Statement
My note:
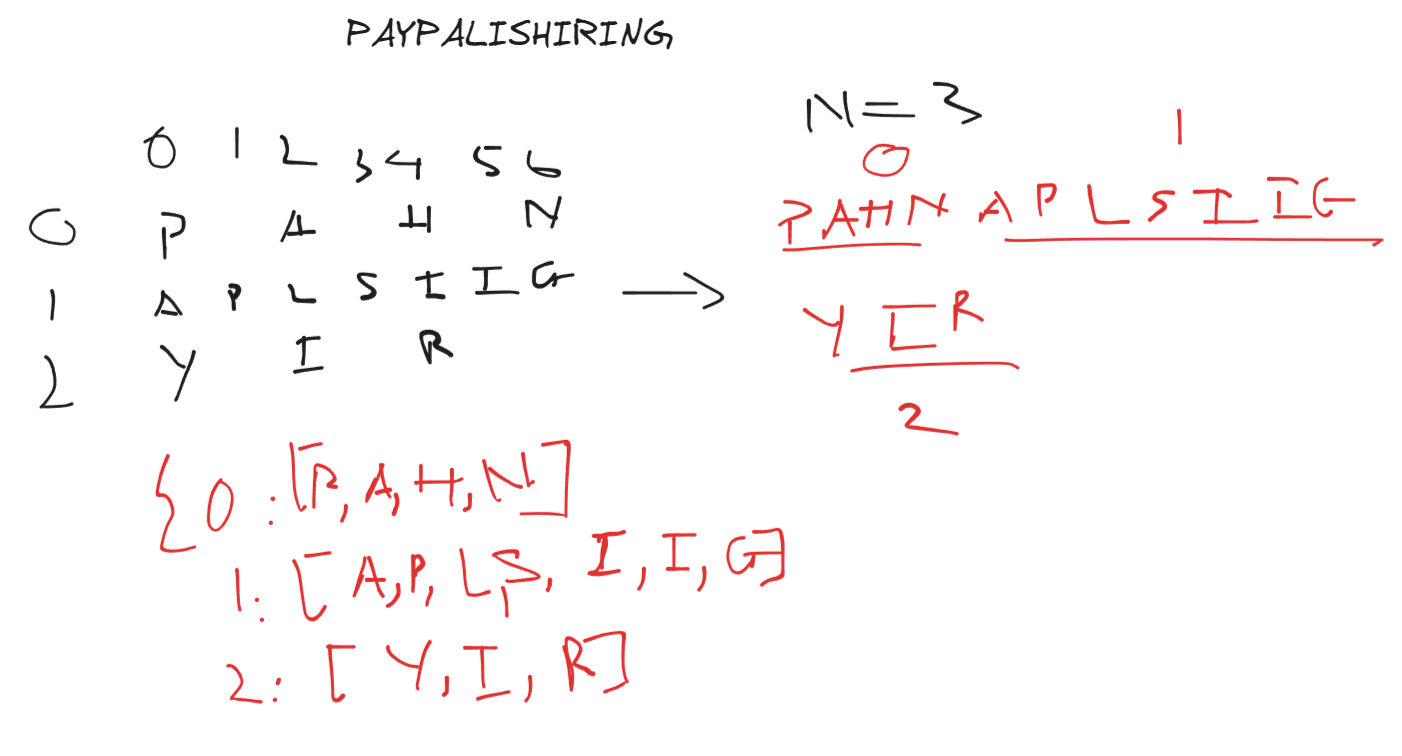
Intuition
My initial thought is to iterate through the input string (s) and organize characters into rows based on the ZigZag pattern defined by the number of rows (numRows). I’ll use a hash_map to store characters for each row, and I need to handle the direction change when reaching the bottom or top row.
Approach
I’ll iterate through each character in the string and place it in the corresponding row based on the ZigZag pattern. I’ll use a defaultdict to efficiently handle rows. The direction will change when reaching the bottom or top row. Finally, I’ll concatenate characters from each row to form the final result.
Complexity
-
Time complexity: O(n), where n is the length of the input string. We iterate through each character once.
-
Space complexity: O(n), as we use a hash_map to store characters in rows, and the final result array has the same length as the input string.
Code
class Solution:
def convert(self, s: str, numRows: int) -> str:
row, col = 0, 0
hash_map = defaultdict(list)
direction = -1
for c in s:
hash_map[row].append(c)
if row == numRows - 1 or row == 0:
direction *= -1
row += direction
res = []
for i in range(len(hash_map)):
res.extend(hash_map[i])
return ''.join(res)
Editorial Solution
Approach 2: String Traversal
class Solution:
def convert(self, s: str, numRows: int) -> str:
if numRows == 1:
return s
answer = []
n = len(s)
chars_in_section = 2 * (numRows - 1)
for curr_row in range(numRows):
index = curr_row
while index < n:
answer.append(s[index])
# If curr_row is not the first or last row,
# then we have to add one more character of current section.
if curr_row != 0 and curr_row != numRows - 1:
chars_in_between = chars_in_section - 2 * curr_row
second_index = index + chars_in_between
if second_index < n:
answer.append(s[second_index])
# Jump to same row's first character of next section.
index += chars_in_section
return "".join(answer)
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)