Problem of The Day: Minimum Cost to Buy Apples
Problem Statement
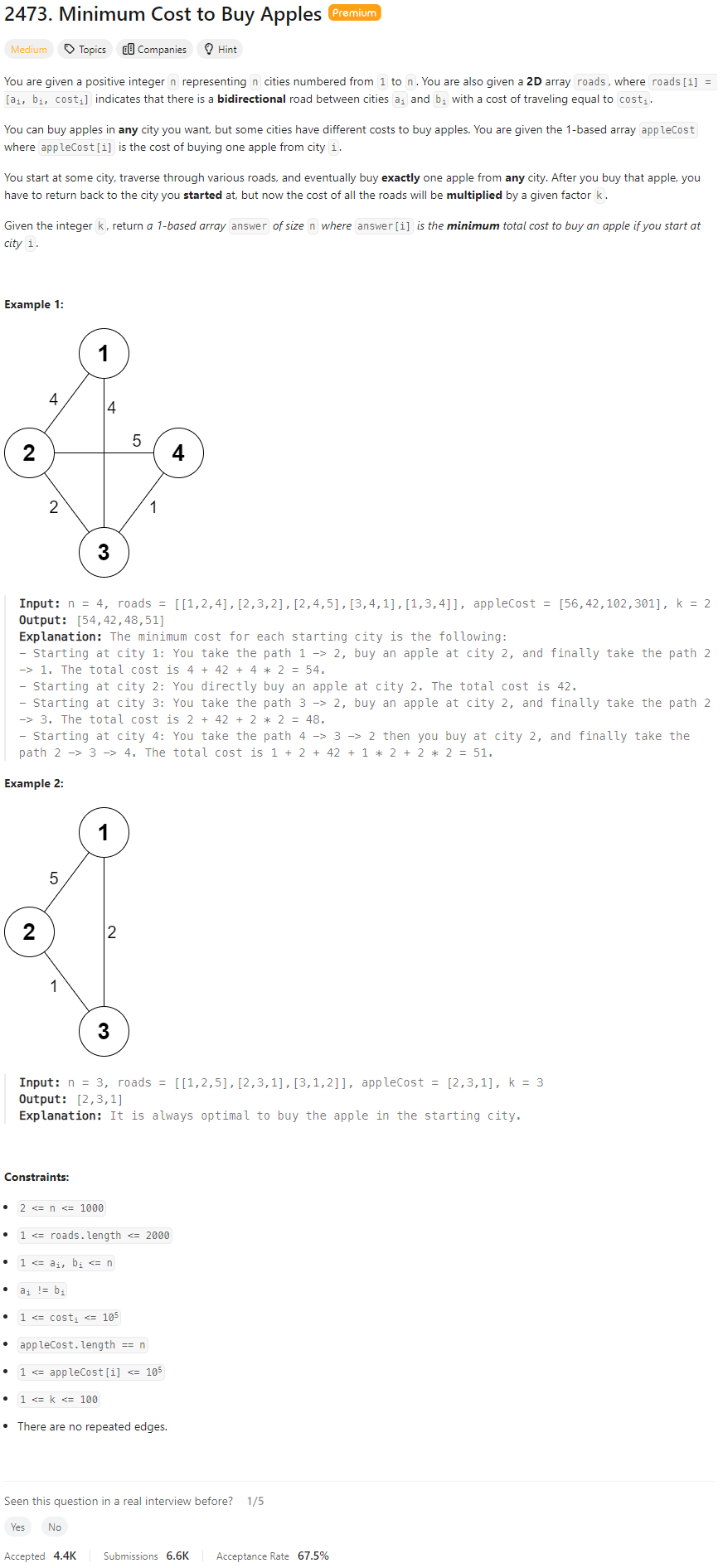
- Note: need to review the Dijkstra’s algorithm to solve the problem
Backtrack Approach - TLE
class Solution:
def minCost(self, n: int, roads: List[List[int]], appleCost: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
res = [float('inf')] * n
graph = {i: [] for i in range(1, n + 1)}
for x, y, cost in roads:
graph[x].append([y, cost])
graph[y].append([x, cost])
minCost = min(appleCost)
dest = appleCost.index(minCost) + 1
def dfs(index):
if index == dest:
return appleCost[index - 1]
ans = float('inf')
for nei, cost in graph[index]:
if nei not in visited:
visited.add(nei)
ans = min(ans, dfs(nei) + cost + k * cost, appleCost[index - 1])
visited.remove(nei)
return ans
for i in range(1, n + 1):
visited = set()
visited.add(i)
res[i - 1] = dfs(i)
return res
Editorial Solution
Approach 1: Shortest Path
Apply modified Dijkstra’s algorithm to solve the problem
class Solution:
def minCost(
self, n: int, roads: List[List[int]], appleCost: List[int], k: int
) -> List[int]:
# Store the graph as a list of lists
# The rows represent the cities (vertices)
# The columns store an adjacency list of road, cost pairs (edge, weight)
graph = [[] for _ in range(n)]
# Add each road to the graph using adjacency lists
# Store each city at `graph[city - 1]`
for city_a, city_b, cost in roads:
graph[city_a - 1].append((city_b - 1, cost))
graph[city_b - 1].append((city_a - 1, cost))
# Finds the minimum cost to buy an apple from the start city
def shortest_path(start_city, graph):
# Stores the travel cost reach each city from the start city
travel_costs = [float("inf") for _ in range(n)]
travel_costs[start_city] = 0
# Initialize the heap (priority queue) with the starting city
# Each element of the heap is a tuple with the cost and city
heap = [(0, start_city)]
min_cost = float("inf")
while heap:
# Remove the city with the minimum cost from the top of the heap
travel_cost, curr_city = heapq.heappop(heap)
# Update the min cost if the curr city has a smaller total cost
min_cost = min(min_cost,
appleCost[curr_city] + (k + 1) * travel_cost)
# Add each neighboring city to the heap if an apple is cheaper
for neighbor, cost in graph[curr_city]:
next_cost = travel_cost + cost
if next_cost < travel_costs[neighbor]:
travel_costs[neighbor] = next_cost
heapq.heappush(heap, (next_cost, neighbor))
return min_cost
# Find the minimum cost to buy an apple starting in each city
ans = []
for start_city in range(0, n):
ans.append(shortest_path(start_city, graph))
return ans
- Time: O(n _ (n + r) _ log n)
- Space: O(n + r)
Approach 2: One Pass Shortest Path
class Solution:
def minCost(
self, n: int, roads: List[List[int]], appleCost: List[int], k: int
) -> List[int]:
# Store the graph as a list of lists
# The rows represent the cities (vertices)
# The columns store an adjacency list of road, cost pairs (edge, weight)
graph = [[] for _ in range(n)]
# Add each road to the graph using adjacency lists
# Store each city at `graph[city - 1]`
for city_a, city_b, cost in roads:
graph[city_a - 1].append((city_b - 1, cost))
graph[city_b - 1].append((city_a - 1, cost))
# Store the cost to buy an apple in each city
# without traveling in the result
result = list(appleCost)
# Initialize the min heap (priority queue) with each starting city
# Each element of the heap is a tuple with the cost and city
heap = [(apple_cost, start_city)
for start_city, apple_cost in enumerate(appleCost)]
heapify(heap)
# Find the minimum cost to buy an apple starting in each city
while heap:
# Remove the city with the minimum cost from the top of the heap
total_cost, curr_city = heapq.heappop(heap)
# If we have already found a path to buy an apple
# for cheaper than the local apple cost, skip this city
if result[curr_city] < total_cost:
continue
# Add each neighboring city to the heap if it is cheaper to
# start there, travel to the current city and buy an apple
# than buy in the neighboring city
for neighbor, cost in graph[curr_city]:
if result[neighbor] > result[curr_city] + (k + 1) * cost:
result[neighbor] = result[curr_city] + (k + 1) * cost
heapq.heappush(heap, (result[neighbor], neighbor))
return result